高级算法——第4周略讲——二叉树
1. 二叉树基本信息
二叉树(Binary Tree)是一种非线性数据结构,代表“祖先”和“后代”的派生关系,体现了“一分为二”的分治逻辑。与链表类似,二叉树的基本单元是节点,每个节点包含值,左子结点引用和右子节点引用。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val:int):
self.val = val # 节点值
self.left = None # 左子节点
self.right = None # 右子节点每个节点都有两个引用(指针)。分别指向左子结点(left-child node)和右子节点(right-child node),该节点被称为这两个子节点的父节点(parent node)。当给定一个二叉树的节点时,我们将该节点的左子结点及其以下节点形成的数称为该节点的左子树(left-subtree),同理可得右子树(right-subtree)。
在二叉树中,除叶节点外,其他所有节点都包含子节点和非空子树。如图所示,如果讲“节点2”视作父节点,则其左子节点和右子节点分别是“节点4”和“节点5”,左子树是“节点4及其以下节点形成的树”,右子树是“节点5及其以下节点形成的树”。
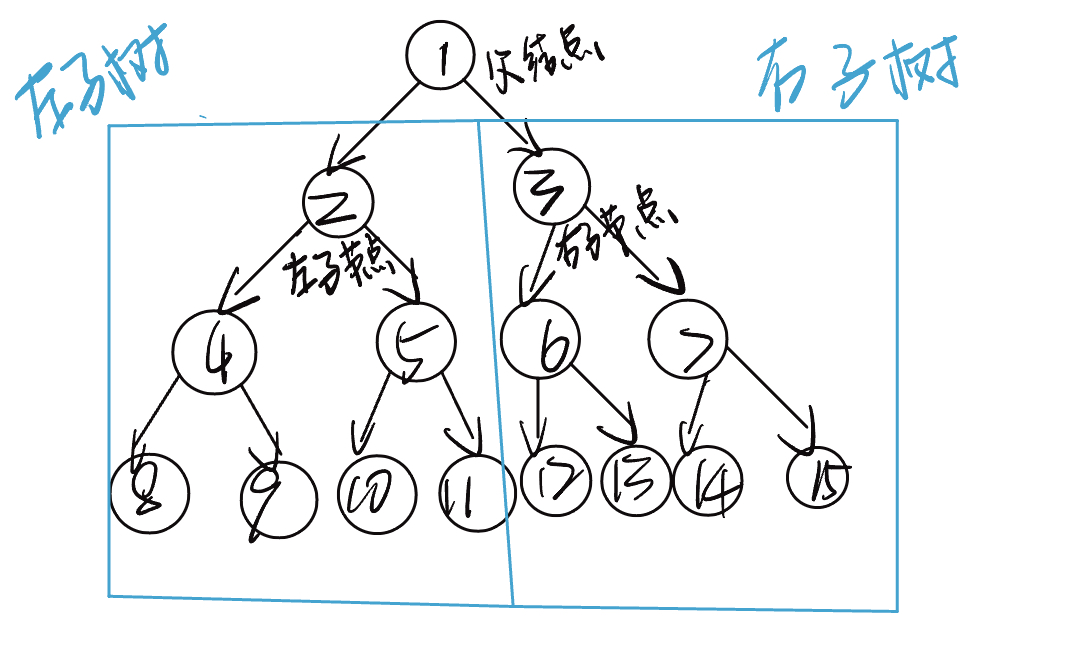
常用术语:
- 根结点(root node):位于二叉树顶层的节点,没有父节点。
- 叶节点(leaf node):没有子节点的节点,其两个指针均指向
None - 边(edge):连接两个节点的线段,即节点引用(指针)。
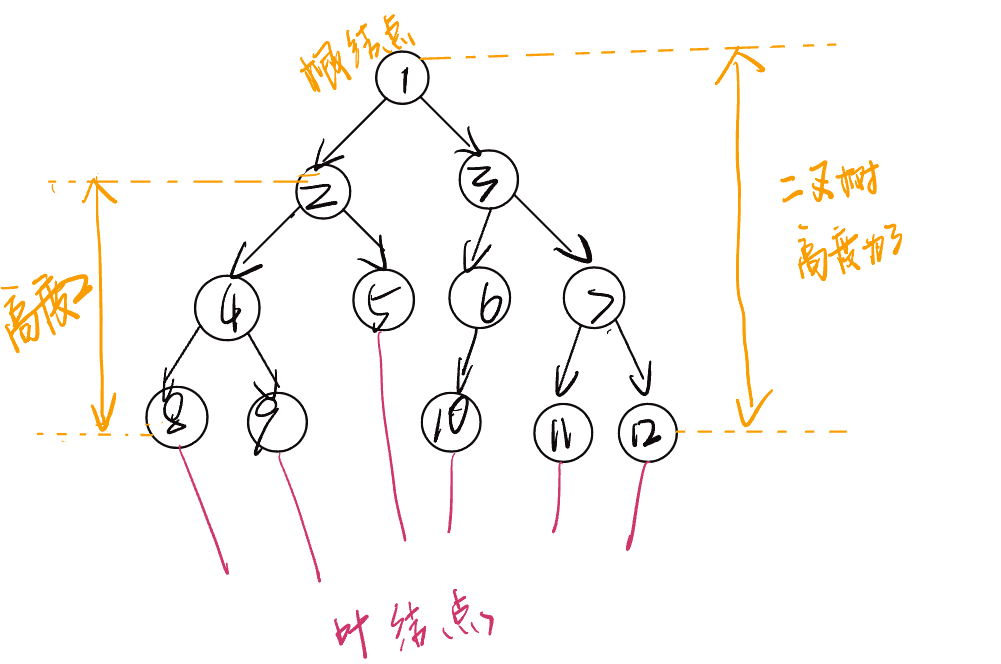
- 节点所在的层(level):从顶至底递增,根结点所在层为 1.
- 二叉树的高度(height):从根节点到最远叶节点所经过的边的数量。
- 节点的度(degree):节点的子节点的数量,在二叉树中,度的取值范围是0、1、2。
- 节点的深度(depth):从根结点到该节点所经历边的数量。
- 节点的高度(height):从距离该节点最远的叶节点到该节点所经过的边的数量。
注意
请注意,我们通常将“高度”和“深度”定义为“经过的边的数量”,但有些题目或教材可能会将其定义为“经过的节点的数量”。在这种情况下,高度和深度都需要加 1 。
2. 二叉树基本操作
2.1 初始化二叉树
与链表类似,首先初始化节点。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val = val # 节点值
self.left = None # 左子节点
self.right = None # 右子节点
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5由 可知以上代码的运行逻辑,即先建立所有节点的子节点并初始化为None,再把相应的子节点一一对应放入。
2.2 插入与删除节点
与链表类似,在二叉树中插入与删除节点可以通过修改指针来实现。
- 下图示意的是插入节点的过程。
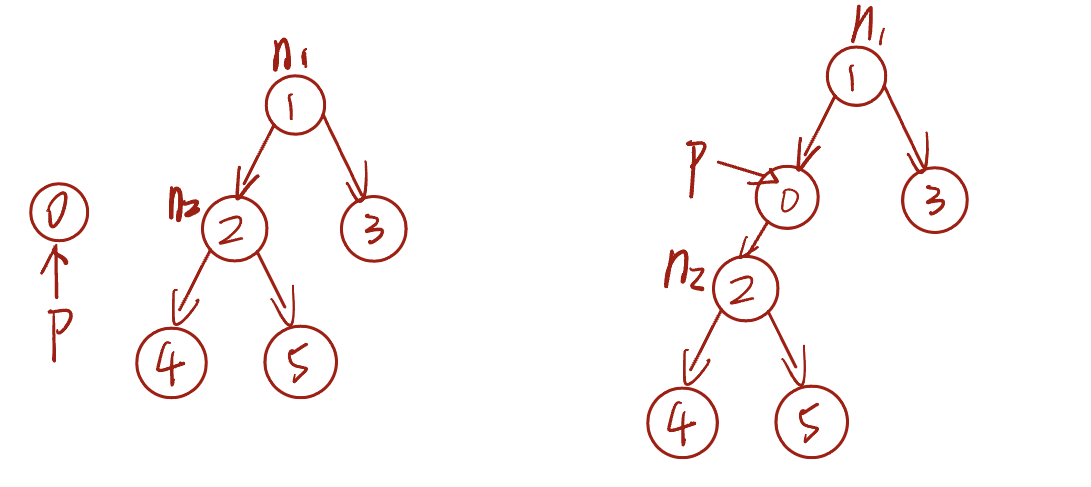
插入节点的代码:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val = val # 节点值
self.left = None # 左子节点
self.right = None # 右子节点
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
p = TreeNode(val=0)
n1.left = n1
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n1.left = p
p.left = n2去掉刚刚添加的节点?
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val = val # 节点值
self.left = None # 左子节点
self.right = None # 右子节点
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
p = TreeNode(val=0)
n1.left = n1
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n1.left = p
p.left = n2
n1.left = n2可视化输出二叉树:
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
def display(root):
"""打印二叉树为字符树"""
lines, *_ = _display_aux(root)
for line in lines:
print(line)
def _display_aux(node):
"""返回包含当前子树所有行的列表,以及子树宽度、高度和水平坐标"""
if node is None:
return [" "], 0, 0, 0
line = f'{node.val}'
width = len(line)
height = 1
middle = width // 2
# 只有左子树
if node.left and not node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width)
shifted_lines = [line + ' ' * width for line in l_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, l_width + width, l_height + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 只有右子树
if not node.left and node.right:
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * (width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
shifted_lines = [' ' * width + line for line in r_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, width + r_width, r_height + 2, width // 2
# 同时有左右子树
if node.left and node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
# 对齐高度
if l_height < r_height:
l_lines += [' ' * l_width] * (r_height - l_height)
elif r_height < l_height:
r_lines += [' ' * r_width] * (l_height - r_height)
merged_lines = [a + ' ' * width + b for a, b in zip(l_lines, r_lines)]
return [first_line, second_line] + merged_lines, l_width + width + r_width, max(l_height, r_height) + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 叶子节点
return [line], width, height, middle
# 示例:创建二叉树并打印
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.right = TreeNode(6)
display(root)/ output
_1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
def display(root):
"""打印二叉树为字符树"""
lines, *_ = _display_aux(root)
for line in lines:
print(line)
def _display_aux(node):
"""返回包含当前子树所有行的列表,以及子树宽度、高度和水平坐标"""
if node is None:
return [" "], 0, 0, 0
line = f'{node.val}'
width = len(line)
height = 1
middle = width // 2
# 只有左子树
if node.left and not node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width)
shifted_lines = [line + ' ' * width for line in l_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, l_width + width, l_height + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 只有右子树
if not node.left and node.right:
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * (width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
shifted_lines = [' ' * width + line for line in r_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, width + r_width, r_height + 2, width // 2
# 同时有左右子树
if node.left and node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
# 对齐高度
if l_height < r_height:
l_lines += [' ' * l_width] * (r_height - l_height)
elif r_height < l_height:
r_lines += [' ' * r_width] * (l_height - r_height)
merged_lines = [a + ' ' * width + b for a, b in zip(l_lines, r_lines)]
return [first_line, second_line] + merged_lines, l_width + width + r_width, max(l_height, r_height) + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 叶子节点
return [line], width, height, middle
# 示例:创建二叉树并打印
# root = TreeNode(1)
# root.left = TreeNode(2)
# root.right = TreeNode(3)
# root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
# root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
# root.right.right = TreeNode(6)
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
p = TreeNode(val=0)
n1.left = n1
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n1.left = p
p.left = n2
display(n1)/ output
1
/ \
_0 3
/
2
/ \
4 5class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
def display(root):
"""打印二叉树为字符树"""
lines, *_ = _display_aux(root)
for line in lines:
print(line)
def _display_aux(node):
"""返回包含当前子树所有行的列表,以及子树宽度、高度和水平坐标"""
if node is None:
return [" "], 0, 0, 0
line = f'{node.val}'
width = len(line)
height = 1
middle = width // 2
# 只有左子树
if node.left and not node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width)
shifted_lines = [line + ' ' * width for line in l_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, l_width + width, l_height + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 只有右子树
if not node.left and node.right:
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * (width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
shifted_lines = [' ' * width + line for line in r_lines]
return [first_line, second_line] + shifted_lines, width + r_width, r_height + 2, width // 2
# 同时有左右子树
if node.left and node.right:
l_lines, l_width, l_height, l_middle = _display_aux(node.left)
r_lines, r_width, r_height, r_middle = _display_aux(node.right)
first_line = ' ' * (l_middle + 1) + '_' * (l_width - l_middle - 1) + line + '_' * r_middle + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle)
second_line = ' ' * l_middle + '/' + ' ' * (l_width - l_middle - 1 + width + r_middle) + '\\' + ' ' * (r_width - r_middle - 1)
# 对齐高度
if l_height < r_height:
l_lines += [' ' * l_width] * (r_height - l_height)
elif r_height < l_height:
r_lines += [' ' * r_width] * (l_height - r_height)
merged_lines = [a + ' ' * width + b for a, b in zip(l_lines, r_lines)]
return [first_line, second_line] + merged_lines, l_width + width + r_width, max(l_height, r_height) + 2, l_width + width // 2
# 叶子节点
return [line], width, height, middle
# 示例:创建二叉树并打印
# root = TreeNode(1)
# root.left = TreeNode(2)
# root.right = TreeNode(3)
# root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
# root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
# root.right.right = TreeNode(6)
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
p = TreeNode(val=0)
n1.left = n1
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n1.left = p
p.left = n2
n1.left = n2
display(n1)/ output
_1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5相关信息
需要注意的是,插入节点可能会改变二叉树的原有逻辑结构,而删除节点通常意味着删除该节点及其所有子树。因此,在二叉树中,插入与删除通常是由一套操作配合完成的,以实现有实际意义的操作。
3. 常见二叉树类型
3.1 完美二叉树
完美二叉树(perfect binary tree)所有层的节点都被完全填满。在完美二叉树中,叶节点的度为0,其余所有节点的度都为2;若树的高度为h,则总节点数为
::: tips
请注意,在中文社区中,完美二叉树又可以称为满二叉树
:::
3.2 完全二叉树
完全二叉树(complete binary tree)只有最底层的节点未被填满,且最底层节点尽量靠左填充。
3.3 完满二叉树
完满二叉树(full binary tree)除了叶节点之外,其余所有节点都有两个子节点。
3.4 平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树(balanced binary tree)中任意节点的左子树和右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
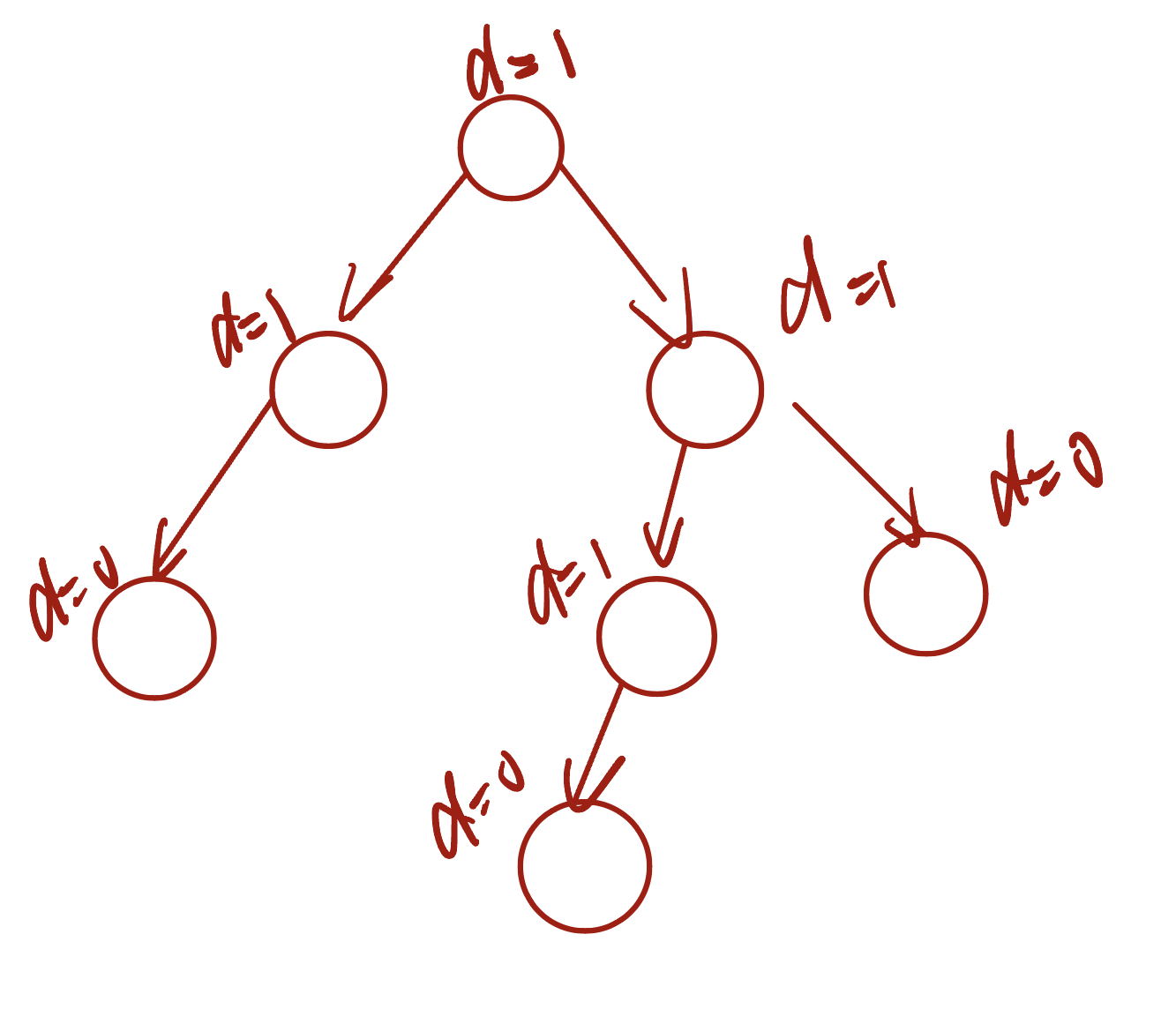
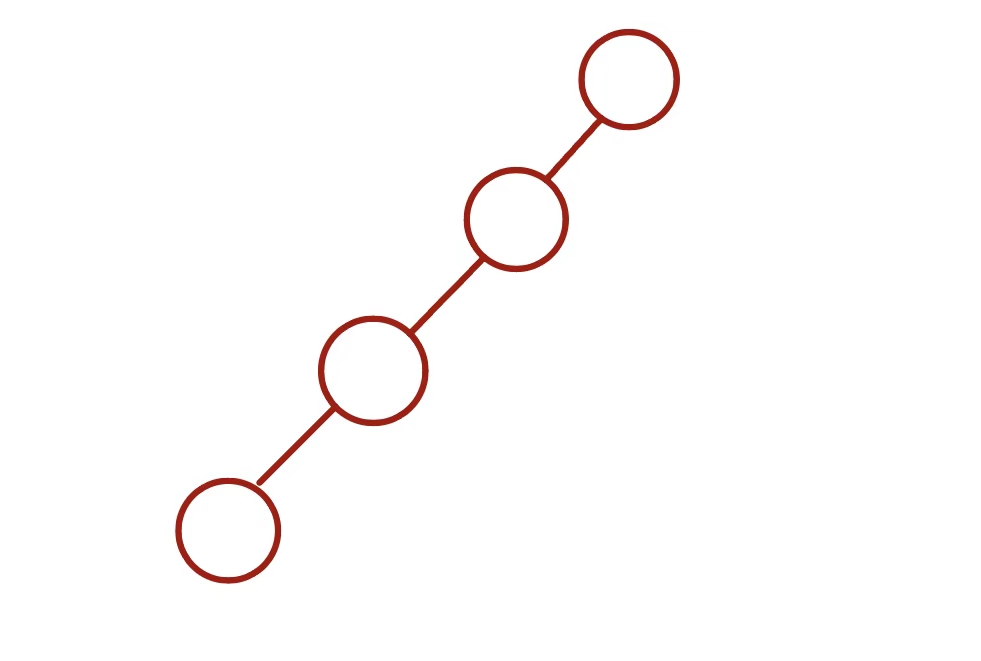
3.5 二叉树退化
当二叉树的每层节点都被填满时,达到“完美二叉树”;当所有节点都偏向一侧时,二叉树退化为“链表”。
- 完美二叉树是理想情况,可以充分发挥二叉树“分治”的优势。
- 链表则是另一个极端,所有操作都变为线性操作,时间复杂度退化至 O(n)。

详情
——chatgpt:
是的,您所上传的图片确实是一个二叉树的形式,虽然从它的结构上看更像是个“退化”的形式。通常情况下,如果二叉树的某些节点只有一个子节点(左子节点或者右子节点),而另一个子节点为空,这样的二叉树被称为“退化二叉树”(或“病态二叉树”)。这会使得树的形状接近于一条线,而不是理想的完全平衡的形状。
从图片来看,这个树的结构比较简洁,每个节点只有一个或者两个子节点,但并没有形成完全的平衡形状。如果这表示一种数据结构,通常会导致某些操作的效率下降,如查找、插入等。
如果您有更多关于二叉树结构的问题,或者需要分析具体的二叉树实现,欢迎进一步探讨。
不完全是一个退化二叉树。
表7-1 二叉树的最佳结构和最差结构
| 完美二叉树 | 链表 | |
|---|---|---|
| 第 | ||
| 高度为 | ||
| 高度为 | ||
| 节点总数为 |
4. 二叉树的遍历
4.1 广度优先遍历 (BFS)
非递归:
from collections import deque
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
def level_order(root):
queue = deque()
queue.append(root)
res = []
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
res.append(node.val)
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
return res
level_order(n1)
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
def printtree(root):
queue = []
queue.append(root)
res = []
while queue:
length = len(queue)
for i in range(length):
node = queue[i]
res.append(node.val)
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
queue = queue[length:]
return res
printtree(n1)class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
def level_order(root):
queue = []
if root is not None:
queue.append(root)
res = []
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
res.append(node)
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
return res
level_order(n1)递归方法:
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
res = []
def level_order(root):
if not res:
res.append(root.val)
if root.left:
res.append(root.left.val)
if root.right:
res.append(root.right.val)
if root.left is not None:
level_order(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
level_order(root.right)
level_order(n1)
print(res)class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
res = []
def level_order_recursive(root):
res = []
if root:
level_helper([root], res)
return res
def level_helper(queue, res):
if not queue:
return
node = queue.pop(0)
res.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
level_helper(queue, res)
level_order_recursive()4.2 深度优先遍历(DFS)
4.2.1 pre order
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
res = []
def pre_order(root):
if root is None:
return
res.append(root.val)
if root.left is not None:
pre_order(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
pre_order(root.right)
pre_order(n1)
print(res)4.2.2 In Order
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
res = []
def in_order(root):
if root is None:
return
if root.left is not None:
in_order(root.left)
res.append(root.val)
if root.right is not None:
in_order(root.right)
in_order(n1)
print(res)4.2.3 Post Order
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val: int = val # 节点值
self.left: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 左子节点引用
self.right: 'TreeNode' | None = None # 右子节点引用
n1 = TreeNode(val=1)
n2 = TreeNode(val=2)
n3 = TreeNode(val=3)
n4 = TreeNode(val=4)
n5 = TreeNode(val=5)
n6 = TreeNode(val=6)
n7 = TreeNode(val=7)
n1.left = n2
n1.right = n3
n2.left = n4
n2.right = n5
n3.left = n6
n3.right = n7
res = []
def post_order(root):
if root is None:
return
if root.left is not None:
post_order(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
post_order(root.right)
res.append(root.val)
post_order(n1)
print(res)5. 二叉树的数组表示
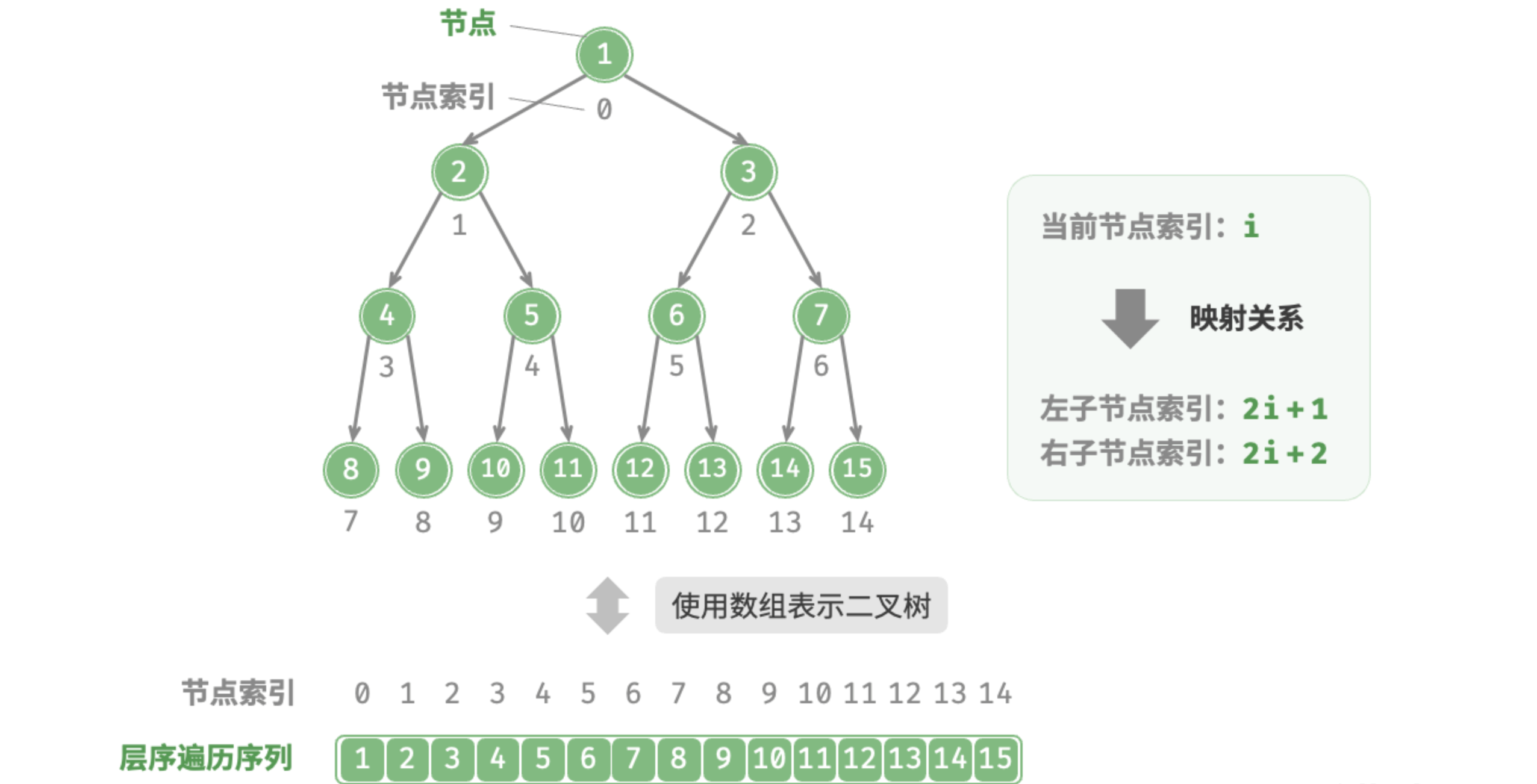
5.1 用二叉树的数组表示实现 BFS DFS
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class ArrayBinaryTree:
"""数组表示下的二叉树类"""
def __init__(self, arr: list[int | None]):
"""构造方法"""
self._tree = list(arr)
def size(self):
"""列表容量"""
return len(self._tree)
def val(self, i: int) -> int:
"""获取索引为 i 节点的值"""
if i < 0 or i >= self.size():
return None
return self._tree[i]
def left(self, i: int) -> int | None:
"""获取左子节点的索引"""
return 2 * i + 1
def right(self, i: int) -> int | None:
"""获取右子节点的索引"""
return 2 * i + 2
def parent(self, i: int) -> int | None:
"""获取父节点的索引"""
return (i - 1) // 2
def level_order(self) -> list[int]:
"""层序遍历"""
self.res = []
# 直接遍历数组
for i in range(self.size()):
if self.val(i) is not None:
self.res.append(self.val(i))
return self.res
def dfs(self, i: int, order: str):
"""深度优先遍历"""
if self.val(i) is None:
return
# 前序遍历
if order == "pre":
self.res.append(self.val(i))
self.dfs(self.left(i), order)
# 中序遍历
if order == "in":
self.res.append(self.val(i))
self.dfs(self.right(i), order)
# 后序遍历
if order == "post":
self.res.append(self.val(i))
def pre_order(self) -> list[int]:
"""前序遍历"""
self.res = []
self.dfs(0, order="pre")
return self.res
def in_order(self) -> list[int]:
"""中序遍历"""
self.res = []
self.dfs(0, order="in")
return self.res
def post_order(self) -> list[int]:
"""后序遍历"""
self.res = []
self.dfs(0, order="post")
return self.res测试代码:
"""Driver Code"""
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 初始化二叉树
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, None, 6, None]
abt = ArrayBinaryTree(arr)
# 访问节点
i = 1
l, r, p = abt.left(i), abt.right(i), abt.parent(i)
# 遍历树
res = abt.level_order()
res = abt.pre_order()
res = abt.in_order()
res = abt.post_order()
print(res)6. 二叉搜索树(BST)
对于根节点,左子树中所有的值 < 根节点 < 右子树中所有的值
任意节点的左右子树也是二叉搜索树,同样满足条件1.
我们将二叉搜索树封装为一个类
BinarySearchTree,并声明一个成员变量 root,指向树的根结点。
6.0 补充知识点——类
6.0.1 类的实例化:
class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
dog = Animal() # 实例化6.0.2 类的函数调用初始化函数的变量:
class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
a = 100
def print(self):
print(a)
dog = Animal() # 实例化
dog.print()
# output
Animal created
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Coder\Lesson\d.py", line 11, in <module>
dog.print()
File "C:\Coder\Lesson\d.py", line 7, in print
print(a)
NameError: name 'a' is not definedclass Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
self.a = 100
def print(self):
print(self.a)
dog = Animal() # 实例化
dog.print()
# output
Animal created
1006.0.2 函数互相之间调用变量
class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
self.a = 1000
def print(self, text):
self.bo = "Shelley"
print(text)
def add_sum(self):
print(self.bo)
dog = Animal() # 实例化
dog.add_sum()
# output
Animal created
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Coder\Lesson\d.py", line 15, in <module>
dog.add_sum()
File "C:\Coder\Lesson\d.py", line 11, in add_sum
print(self.bo)
AttributeError: 'Animal' object has no attribute 'bo'报错了!因为我们没有调用 self.bo 被定义的函数 print,我们调用 print 之后再调用 add_sum试试。
class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
self.a = 1000
def print(self, text):
self.bo = "Shelley"
print(text)
def add_sum(self):
print(self.bo)
dog = Animal() # 实例化
dog.print(text = "dog")
dog.add_sum()
# output
Animal created
dog
Shelley6.0.3 类的实例化调用类中变量
class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
self.a = 1000
def print(self):
print(self.a)
dog = Animal() # 实例化
print(dog.a)
# output
Animal created
1000class Animal():
def __init__(self): # 初始化函数,可有可没有
print("Animal created")
self.a = 1000
def print(self):
print(self.a)
self.b = 1
dog = Animal() # 实例化
print(dog.a)
print(dog.b)
# output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Coder\Lesson\d.py", line 13, in <module>
print(dog.b)
AttributeError: 'Animal' object has no attribute 'b'
Animal created
10006.1 查找节点
给定目标节点值
num,可以根据二叉搜索树的性质来查找。我们声明一个节点
cur,从二叉树的根节点 root 出发。- 若
cur.val < num,说明目标节点在 cur 的右子树中,因此执行cur = cur.right - 若
cur.val > num,说明目标节点在 cur 的左子树中,因此执行cur = cur.left - 若
cur.val = num,说明目标节点就是num
- 若
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def search(self, root, val):
if root is None:
return None
if val < root.val:
return self.search(root.left, val)
elif val > root.val:
return self.search(root.right, val)
else:
return root # 这里是返回了该节点的地址,而不是值
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 手动创建二叉搜索树
bst = BST()
bst.root = TreeNode(4)
bst.root.left = TreeNode(2)
bst.root.right = TreeNode(6)
bst.root.left.left = TreeNode(1)
bst.root.left.right = TreeNode(3)
bst.root.right.left = TreeNode(5)
bst.root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
# 测试查找节点
node = bst.search(bst.root, 7)
if node:
print(f"找到了节点,值为: {node.val}") # 打印该节点的值
else:
print("未找到节点")class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self._root = None
def search(self,val):
cur = self._root
while cur:
if cur.val > val:
cur = cur.left
elif cur.val < val:
cur = cur.right
else:
break
return cur
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 手动创建二叉搜索树
bst = BST()
bst.root = TreeNode(4)
bst.root.left = TreeNode(2)
bst.root.right = TreeNode(6)
bst.root.left.left = TreeNode(1)
bst.root.left.right = TreeNode(3)
bst.root.right.left = TreeNode(5)
bst.root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
# 测试查找节点
node = bst.search(bst.root, 9)
if node:
print(f"找到了节点,值为: {node.val}") # 打印该节点的值
else:
print("未找到节点")6.2 插入节点
给定一个待插入元素
num,为了保持二叉搜索树“左子树 < 根节点 < 右子树”的性质:查找插入位置:与查找操作相似,从根节点出发,根据当前节点值和
num的大小关系循环向下搜索,直到越过叶节点(遍历至 None )时跳出循环。在该位置插入节点:初始化节点
num,将该节点置于 None 的位置。
注意
在代码实现中,需要注意以下两点。
二叉搜索树不允许存在重复节点,否则将违反其定义。因此,若待插入节点在树中已存在,则不执行插入,直接返回。
为了实现插入节点,我们需要借助节点 pre 保存上一轮循环的节点。这样在遍历至 None 时,我们可以获取到其父节点,从而完成节点插入操作。
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def search(self, root, val):
if root is None:
return None
if val < root.val:
return self.search(root.left, val)
elif val > root.val:
return self.search(root.right, val)
else:
return root # 这里是返回了该节点的地址,而不是值
def insert(self, root, num):
if root is None:
return TreeNode(num)
if num < root.val:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, num) # 二叉树找寻路径:根->左->右....
elif num > root.val:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, num)
return root # 返回原二叉树
if __name__ == '__main__':
bst = BST()
bst.root = bst.insert(bst.root,6)
bst.insert(bst.root, 3)
bst.insert(bst.root, 9)
bst.insert(bst.root, 1)
bst.insert(bst.root, 2)
bst.insert(bst.root, 7)
# 测试查找节点
node = bst.search(bst.root, 3)
if node:
print(f"找到了节点,值为: {node.val}") # 打印该节点的值
else:
print("未找到节点")class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self._root = None
def search(self, val):
cur = self._root
while cur:
if cur.val > val:
cur = cur.left
elif cur.val < val:
cur = cur.right
else:
break
return cur
def insert(self, num):
if self._root is None:
self._root = TreeNode(num)
return
cur, pre = self._root, None
while cur is not None:
# 找到重复节点,直接返回
if cur.val == num:
return
pre = cur
# 查找到需要插入的位置
if cur.val < num:
cur = cur.right
else:
cur = cur.left
# 插入节点
node = TreeNode(num)
if pre.val < num:
pre.right = node
else:
pre.left = node
if __name__ == '__main__':
bst = BST()
bst.insert(6)
bst.insert(3)
bst.insert(9)
bst.insert(1)
bst.insert(2)
bst.insert(7)
# 测试查找节点
node = bst.search(7)
if node:
print(f"找到了节点,值为: {node.val}") # 打印该节点的值
else:
print("未找到节点")6.3 删除节点
先在二叉树中查找到目标节点,再将其删除。与插入节点类似,我们需要保证在删除操作完成后,二叉搜索树的“左子树 < 根节点 < 右子树”的性质仍然满足。因此,我们根据目标节点的子节点数量,分 0、1 和 2 三种情况,执行对应的删除节点操作。
当待删除节点的度为 0 时,表示该节点是叶节点,可以直接删除。
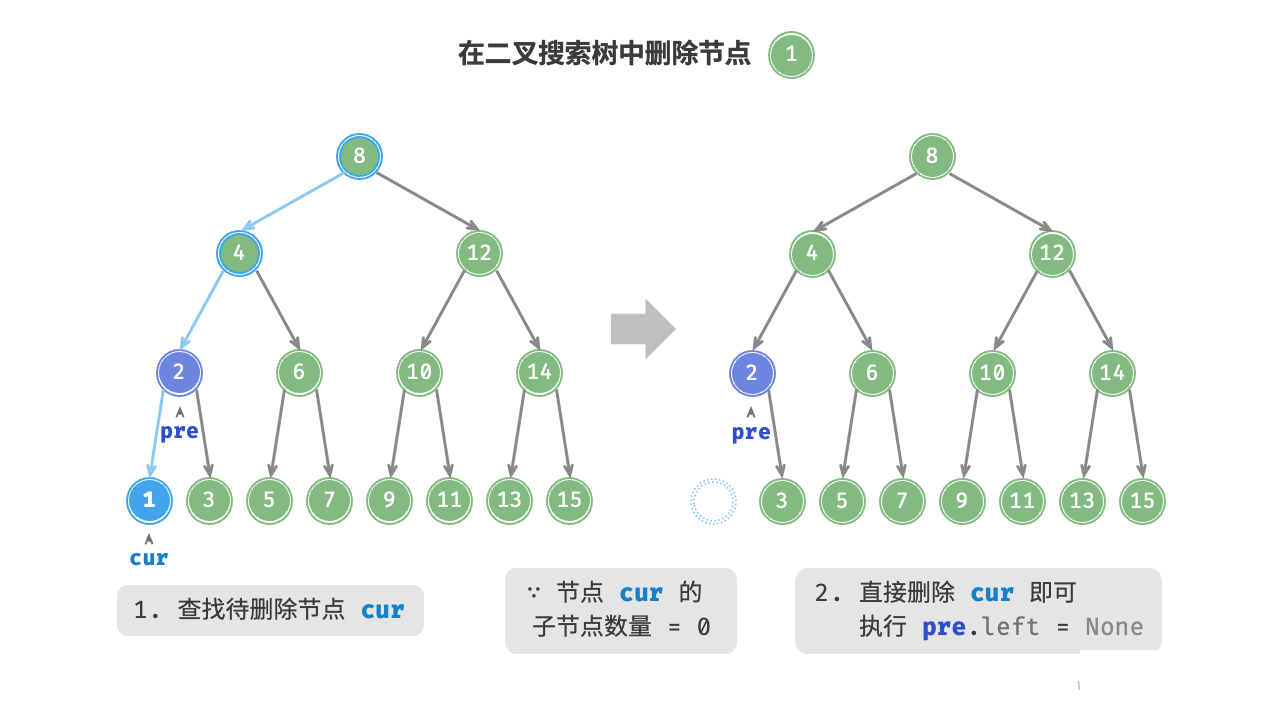
当待删除节点的度为 1 时,将待删除节点替换为其子节点即可。
当待删除节点的度为 2 时,我们无法直接删除它,而需要使用一个节点替换该节点。由于要保持二叉搜索树“左子树 < 根节点 < 右子树”的性质,因此这个节点可以是右子树的最小节点或左子树的最大节点。
class TreeNode:
"""二叉树节点类"""
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
class BST:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def search(self, root, val):
if root is None:
return None
if val < root.val:
return self.search(root.left, val)
elif val > root.val:
return self.search(root.right, val)
else:
return root # 这里是返回了该节点的地址,而不是值
def insert(self, root, num):
if root is None:
return TreeNode(num)
if num < root.val:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, num)
elif num > root.val:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, num)
return root
def delete(self, root, key):
if root is None:
return root
if root.val > key:
root.left = self.delete(root.left, key)
elif root.val < key:
root.right = self.delete(root.right, key)
else:
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return None
elif root.left is None:
return root.right
elif root.right is None:
return root.left
else:
"""找到右子树最小节点"""
min_larger_root = self.find_min(root.right)
root.val = min_larger_root.val
root.right = self.delete(root.right, min_larger_root.val)
return root
# store = root.right
# while store.left is not None:
# store = store.left
# store.left = root.left
# store.right = root.right
# return store
def find_min(self, root):
current = root
while current is not None:
current = current.left
return current
if __name__ == '__main__':
bst = BST()
bst.root = bst.insert(bst.root,6)
bst.insert(bst.root, 3)
bst.insert(bst.root, 9)
bst.insert(bst.root, 1)
bst.insert(bst.root, 2)
bst.insert(bst.root, 7)
bst.delete(bst.root, 7)
# 测试查找节点
node = bst.search(bst.root, 2)
if node:
print(f"找到了节点,值为: {node.val}") # 打印该节点的值
else:
print("未找到节点")def remove(self, num: int):
"""删除节点"""
# 若树为空,直接提前返回
if self._root is None:
return
# 循环查找,越过叶节点后跳出
cur, pre = self._root, None
while cur is not None:
# 找到待删除节点,跳出循环
if cur.val == num:
break
pre = cur
# 待删除节点在 cur 的右子树中
if cur.val < num:
cur = cur.right
# 待删除节点在 cur 的左子树中
else:
cur = cur.left
# 若无待删除节点,则直接返回
if cur is None:
return
# 子节点数量 = 0 or 1
if cur.left is None or cur.right is None:
# 当子节点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子节点
child = cur.left or cur.right
# 删除节点 cur
if cur != self._root:
if pre.left == cur:
pre.left = child
else:
pre.right = child
else:
# 若删除节点为根节点,则重新指定根节点
self._root = child
# 子节点数量 = 2
else:
# 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个节点
tmp: TreeNode = cur.right
while tmp.left is not None:
tmp = tmp.left
# 递归删除节点 tmp
self.remove(tmp.val)
# 用 tmp 覆盖 cur
cur.val = tmp.val6.4 补充内容
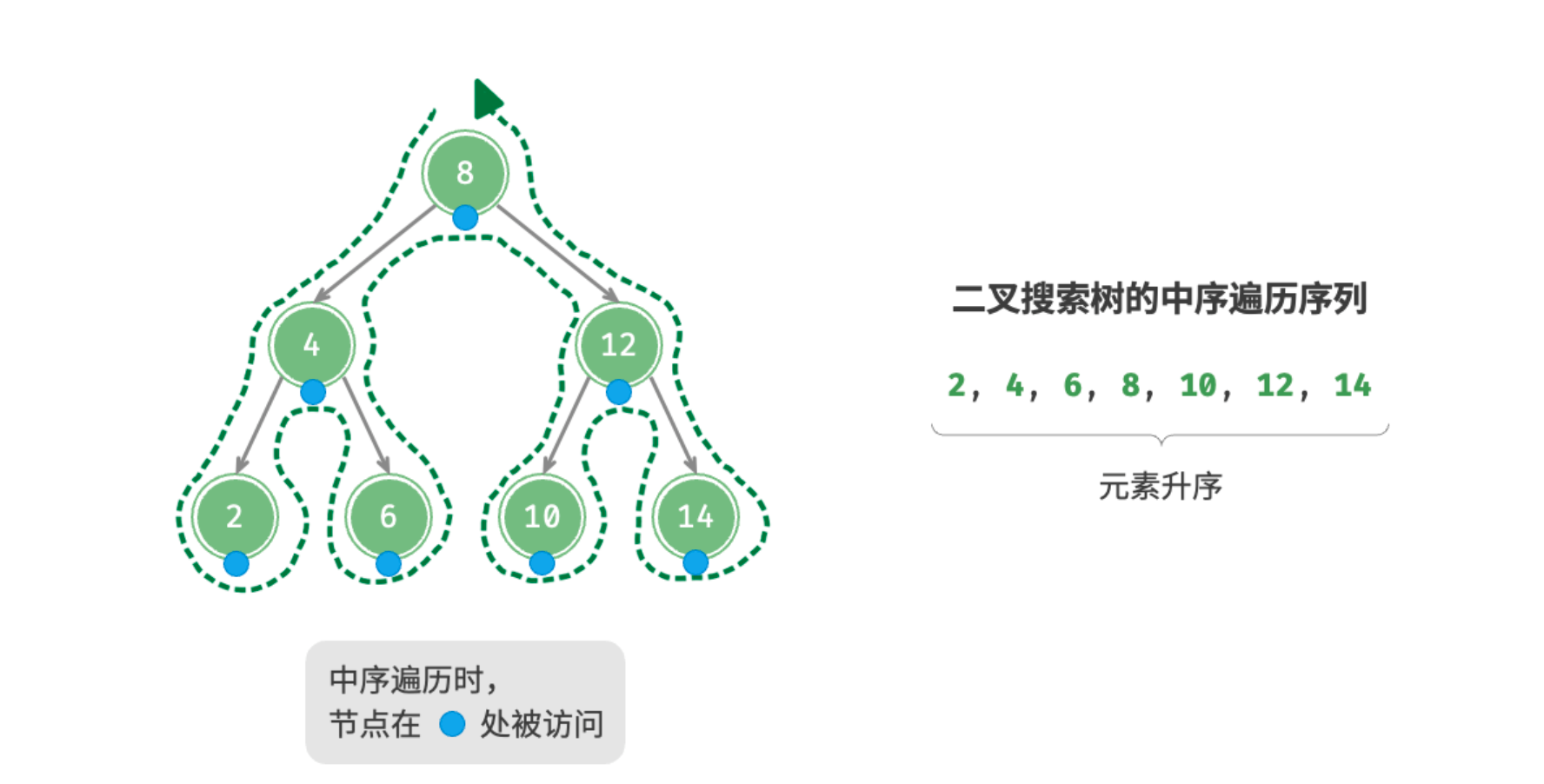
6.4.1 中序遍历有序
如图 7-22 所示,二叉树的中序遍历遵循“左
这意味着在二叉搜索树中进行中序遍历时,总是会优先遍历下一个最小节点,从而得出一个重要性质:二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列是升序的。
利用中序遍历升序的性质,我们在二叉搜索树中获取有序数据仅需
6.4.2 二叉搜索树的效率
给定一组数据,我们考虑使用数组或二叉搜索树存储。观察表 7-2 ,二叉搜索树的各项操作的时间复杂度都是对数阶,具有稳定且高效的性能。只有在高频添加、低频查找删除数据的场景下,数组比二叉搜索树的效率更高。
表 7-2 数组与搜索树的效率对比
| 无序数组 | 二叉搜索树 | |
|---|---|---|
| 查找元素 | ||
| 插入元素 | ||
| 删除元素 |
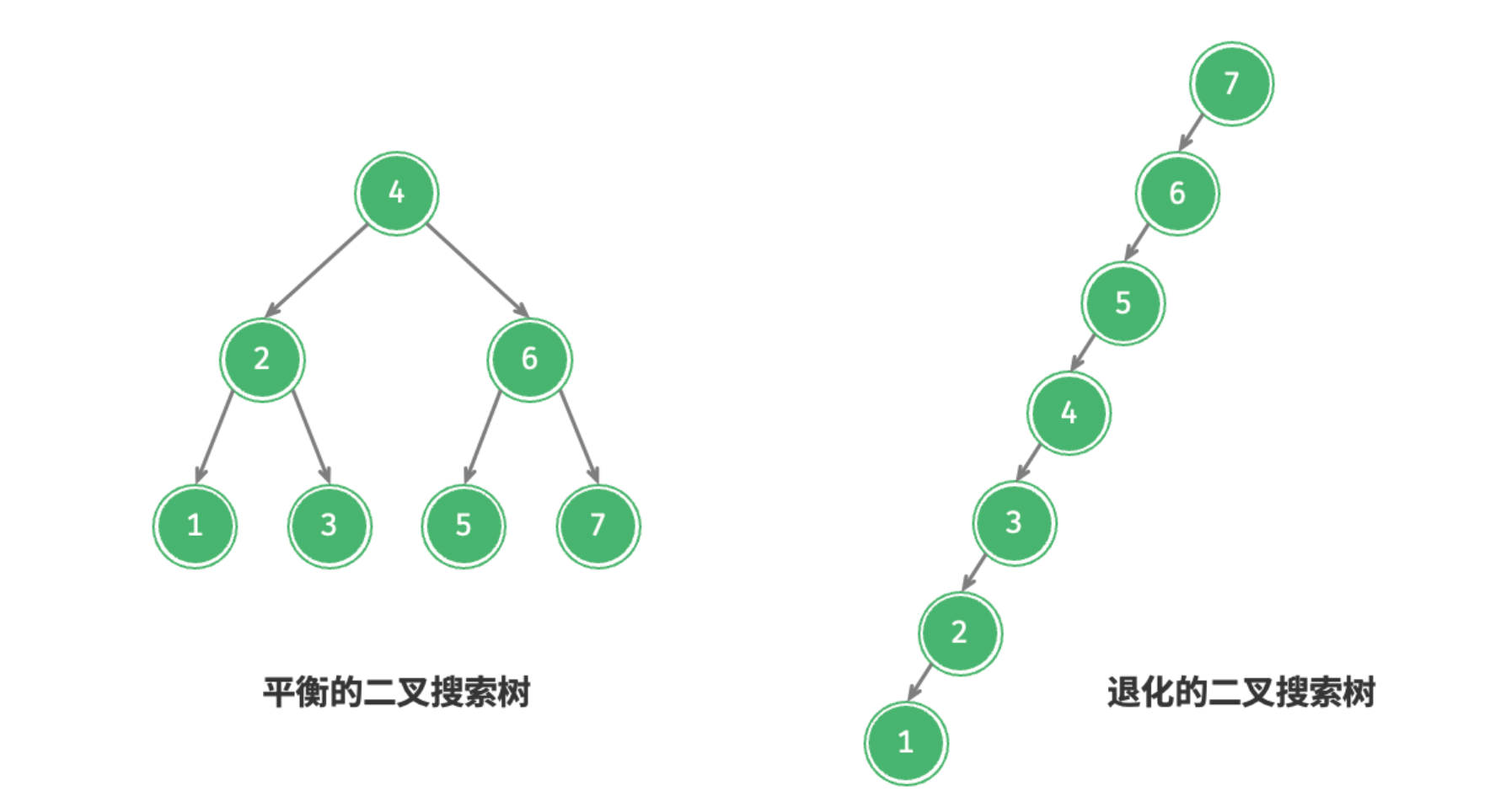
在理想情况下,二叉搜索树是“平衡”的,这样就可以在
然而,如果我们在二叉搜索树中不断地插入和删除节点,可能导致二叉树退化为图 7-23 所示的链表,这时各种操作的时间复杂度也会退化为
6.5 二叉树的常见应用
- 用作系统中的多级索引,实现高效的查找,插入,删除等操作
- 作为某些搜索算法的底层数据结构
- 用于存储数据流,以保持其有序状态
7. 二叉树的时间复杂度
- 什么是二叉树?
二叉树是一个树形结构,其中每个节点最多有两个子节点:一个左子节点和一个右子节点。一个常见的例子是二叉搜索树,它的性质是:对于每个节点,左子树的所有节点值都小于这个节点的值,右子树的所有节点值都大于这个节点的值。
- 树的高度是什么?
树的高度指的是从根节点到最深的叶子节点的路径长度。比如:
- 如果一个二叉树只有一个节点,树的高度是 0。
- 如果一个二叉树有两个节点,根节点和一个叶子节点,那么树的高度是 1。
在一个理想的平衡二叉树中,如果有 n 个节点,那么树的高度大约是
- 为什么是
假设你有一棵平衡的二叉树,并且它的高度为 h,那么这棵树最多可以容纳的节点数是
- 高度为 1 时,最多有 1 个节点(
- 高度为 2 时,最多有 3 个节点(
- 高度为 3 时,最多有 7 个节点(
可以看到,随着树的高度增加,节点的数量呈指数级增长。
要插入、查找或删除一个节点时,你需要从树的根开始,逐层往下找到合适的位置。每向下一层,树的节点数就会减半。换句话说,你在查找的过程中,每一步都缩小了一半的范围。因此,这种操作的时间复杂度是与树的高度成正比的。
对于一个有 n 个节点的平衡二叉树,树的高度大约是
- 总结
- 二叉树操作的时间复杂度通常和树的高度有关。
- 对于一个有
n个节点的平衡二叉树,树的高度大约是 - 查找、插入、删除操作的复杂度都与树的高度相关,所以在平衡二叉树中的这些操作通常为
在二叉树的时间复杂度为
为什么底数是 2?
这是因为在每一层,平衡二叉树的节点数会 翻倍。具体来说:
- 在树的第 0 层(根节点),有 1 个节点。
- 在树的第 1 层,有 2 个节点。
- 在树的第 2 层,有 4 个节点。
- 在树的第 3 层,有 8 个节点。
因此,树的每一层的节点数以
不过,计算机科学中的对数复杂度通常忽略底数,因为不同底数的对数之间的差别只是一个常数倍,并不会影响大规模情况下的渐进复杂度。因此,常常简写为
8. AVL 树
“节点高度”是指从该节点到它的最远叶节点的距离,即所经过的“边”的数量。需要特别注意的是,叶节点的高度为 0
,而空节点的高度为 -1 。我们将创建两个工具函数,分别用于获取和更新节点的高度:
提示
AVL 树的平衡因子的绝对值不可以大于1
8.1 初始化一个 AVL 树
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.height = 0 # 由于 AVL 树的相关操作需要获取节点高度,因此我们需要为节点类添加 height 变量
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 节点的高度:是指从该节点到它最远叶节点的距离,即桥经过的“边”的数量。
# 需要特别注意的是:叶节点的高度为 0,而空节点的高度为 -1,我们将创建两个工具函数,分别用于获取和更新节点的高度
def get_height(self, node):
if node is not None:
return node.height
return -1
def update_height(self, node):
node.height = max([self.height(node.left), self.height(node.right)]) + 1
# target = []
# target.append(self.height(node.left))
# target.append(self.height(node.right))
# node.height = max(target) + 1
# 节点平衡因子
# 节点的平衡因子(balance factor)定义为节点左子树的高度减去节点右子树的高度,同时规定空节点平衡因子为 0
# 我们同样将获取节点的平衡因子的功能封装成函数,方便后续使用
def balance_factor(self, node):
# 空节点平衡因子为 0
if node is None:
return 0
# 节点的平衡因子 = 左子树高度 - 右子树高度
return self.get_height(node.left) - self.get_height(node.right)8.2 AVL 树的旋转
AVL 树的特点在于“旋转”的操作,它能够在不影响二叉树的中序遍历序列的前提下,使失衡的节点重新恢复平衡。换一句话说:旋转操作既能保持“二叉搜索树”的性质,也能使树重新变为“平衡二叉树”。
我们现将平衡因子的绝对值 > 1 的节点称为 “失衡节点” ,根据节点失衡情况不同,旋转操作分为四种:右旋,左旋,先右旋再左旋,先左旋再右旋。
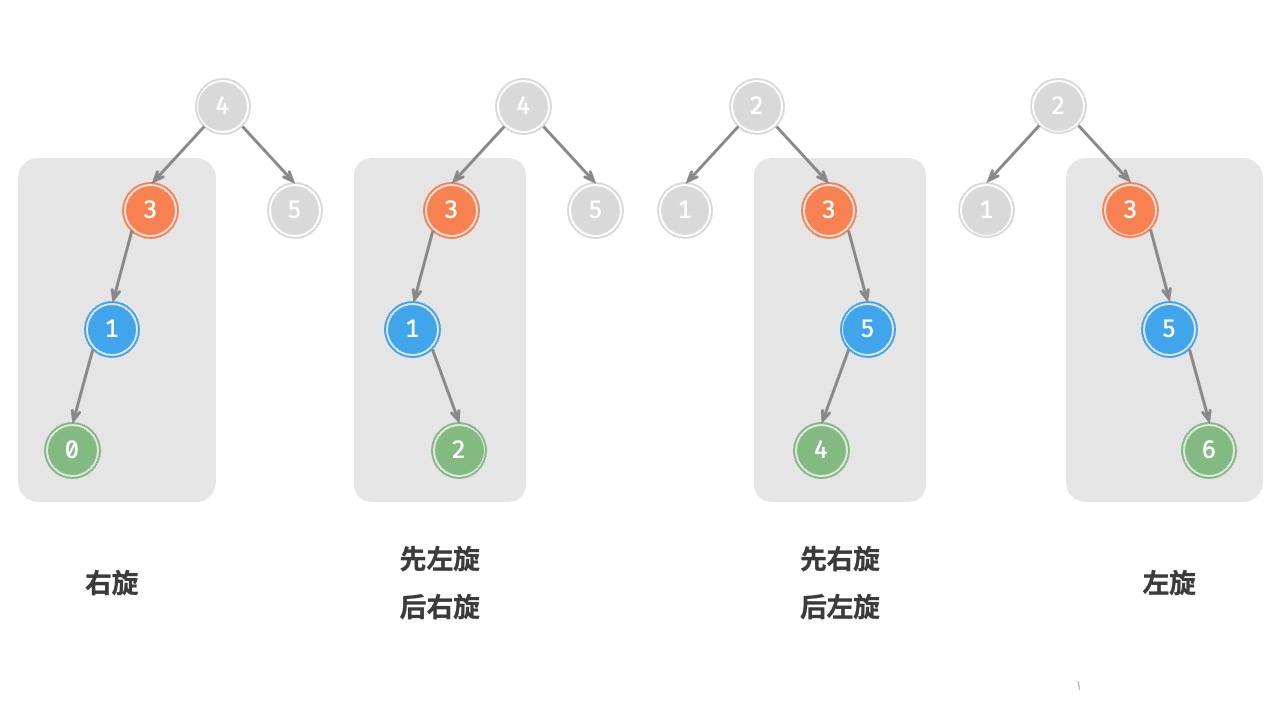
8.2.1 右旋
节点下方为平衡因子。从底至顶看,二叉树中首个失衡节点是“节点 3”。我们关注以该失衡节点为根节点的子树,将该节点记为 node ,其左子节点记为 child ,执行“右旋”操作。完成右旋后,子树恢复平衡,并且仍然保持二叉搜索树的性质。
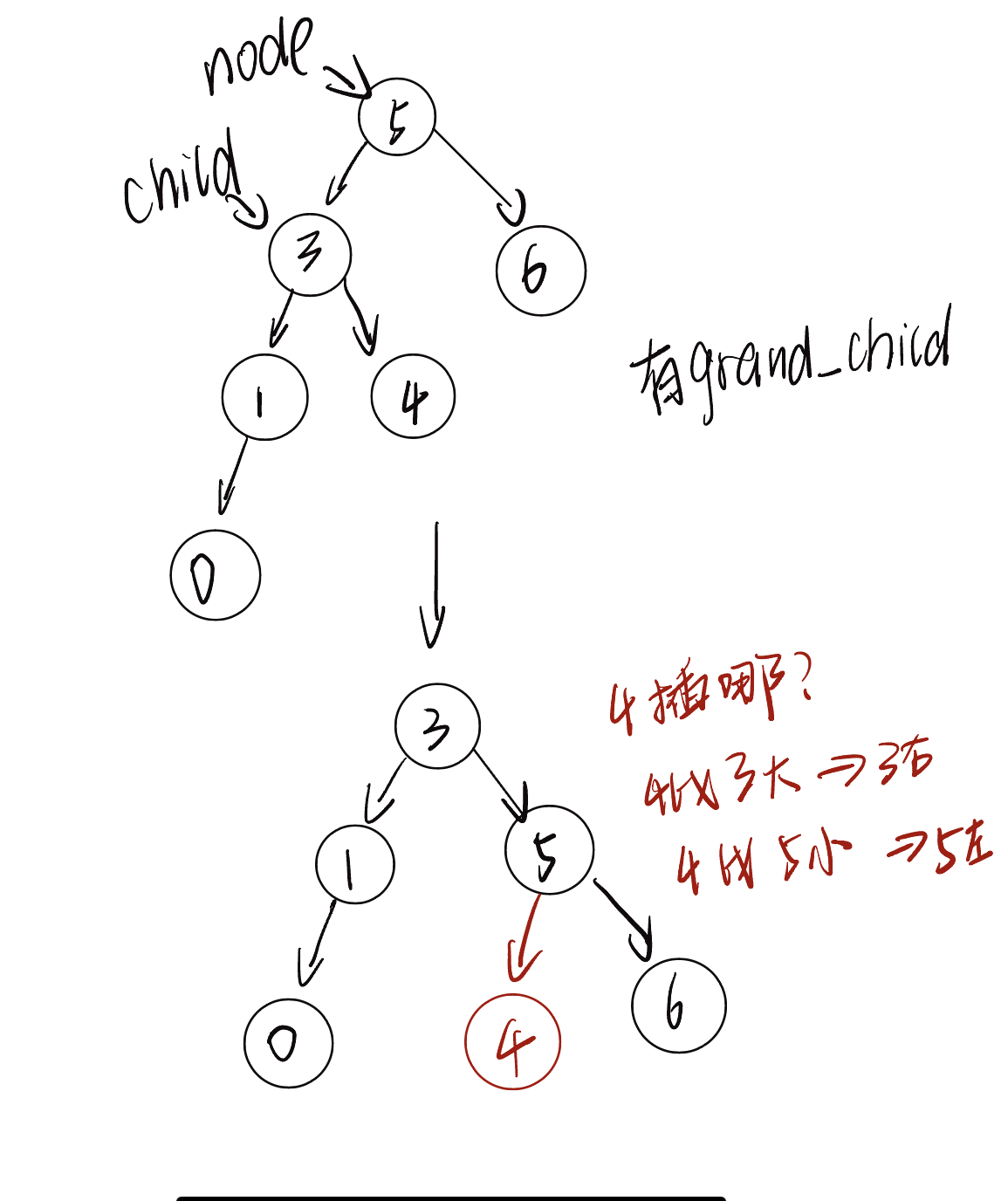
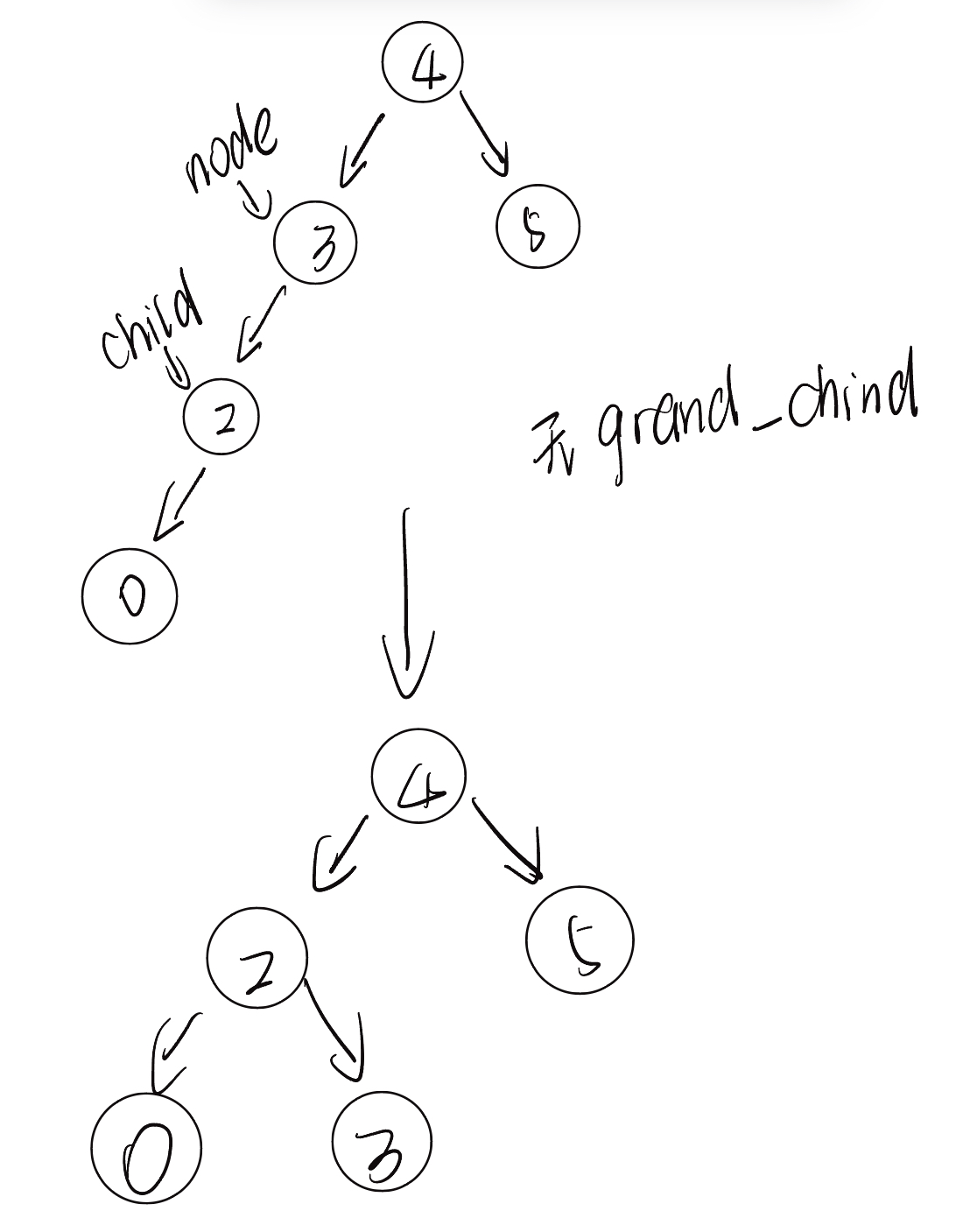
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.height = 0 # 由于 AVL 树的相关操作需要获取节点高度,因此我们需要为节点类添加 height 变量
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 节点的高度:是指从该节点到它最远叶节点的距离,即桥经过的“边”的数量。
# 需要特别注意的是:叶节点的高度为 0,而空节点的高度为 -1,我们将创建两个工具函数,分别用于获取和更新节点的高度
def get_height(self, node):
if node is not None:
return node.height
return -1
def update_height(self, node):
node.height = max([self.height(node.left), self.height(node.right)]) + 1
# target = []
# target.append(self.height(node.left))
# target.append(self.height(node.right))
# node.height = max(target) + 1
# 节点平衡因子
# 节点的平衡因子(balance factor)定义为节点左子树的高度减去节点右子树的高度,同时规定空节点平衡因子为 0
# 我们同样将获取节点的平衡因子的功能封装成函数,方便后续使用
def balance_factor(self, node):
# 空节点平衡因子为 0
if node is None:
return 0
# 节点的平衡因子 = 左子树高度 - 右子树高度
return self.get_height(node.left) - self.get_height(node.right)
def right_rotate(self, node):
child = node.left
grand_child = child.right # 若没有就记成 None。
child.right = node
node.left = grand_child
self.update_height(node)
self.update_height(child)
return child8.2.2 左旋
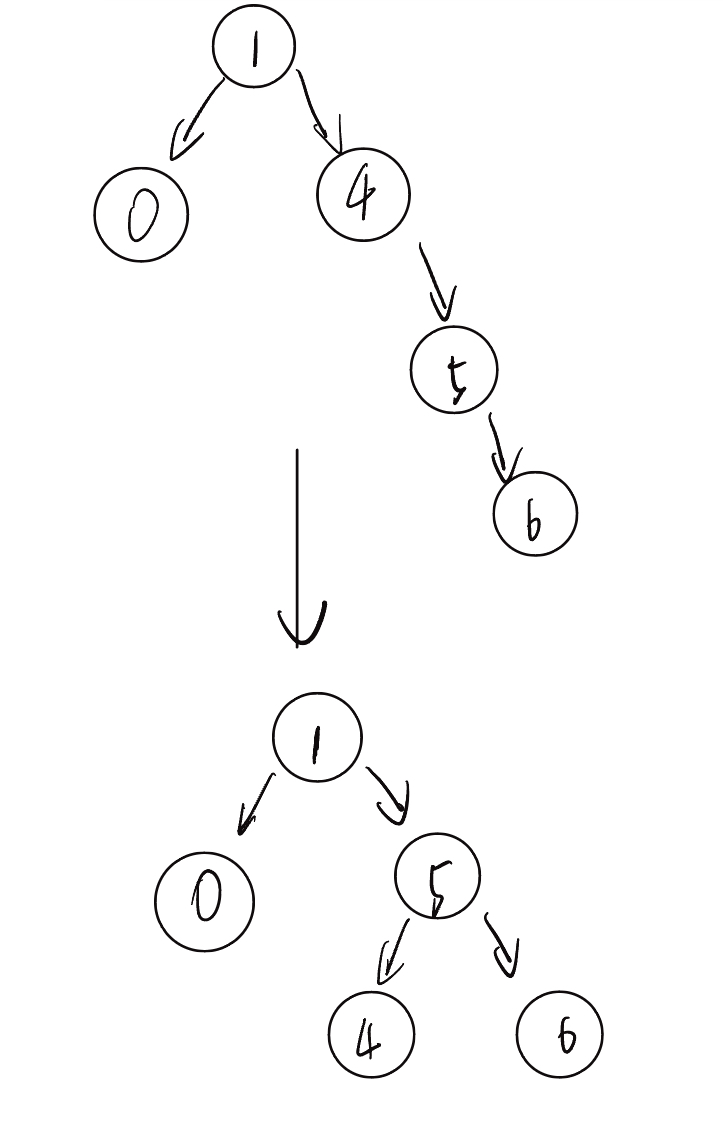
4 是 node
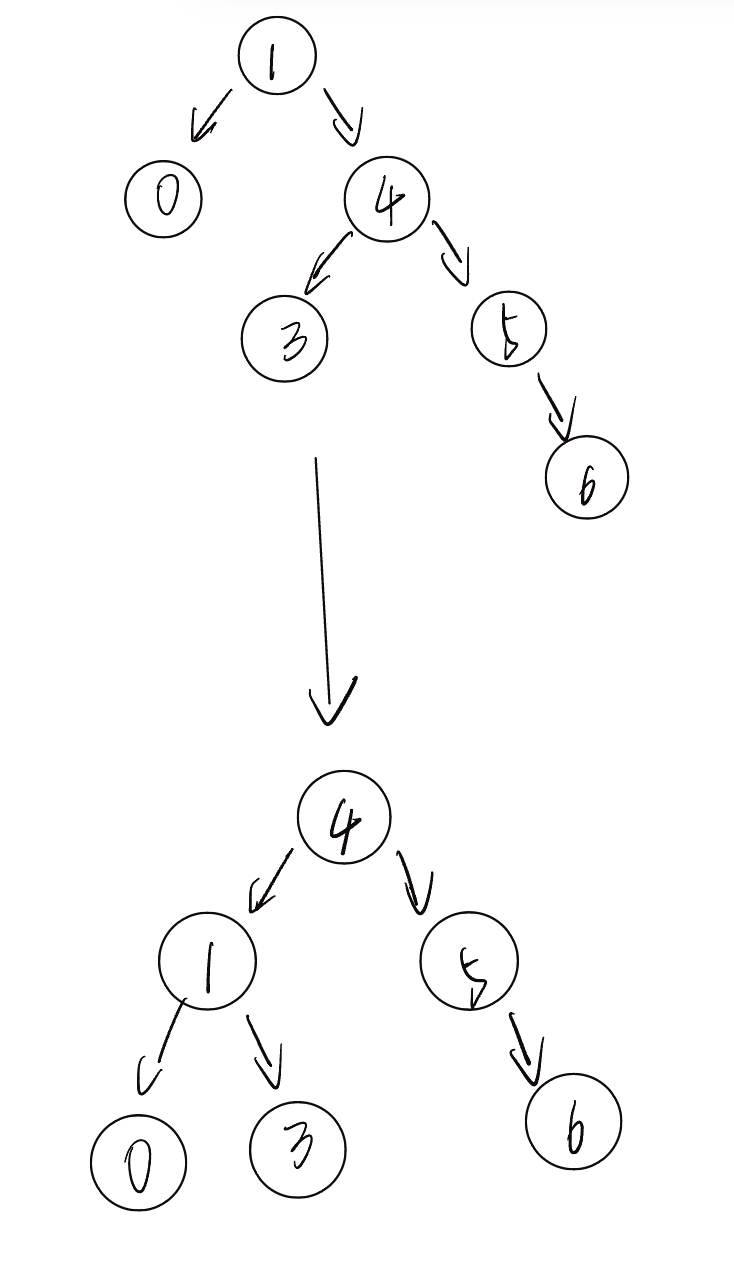
1 是 node
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.height = 0 # 由于 AVL 树的相关操作需要获取节点高度,因此我们需要为节点类添加 height 变量
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 节点的高度:是指从该节点到它最远叶节点的距离,即桥经过的“边”的数量。
# 需要特别注意的是:叶节点的高度为 0,而空节点的高度为 -1,我们将创建两个工具函数,分别用于获取和更新节点的高度
def get_height(self, node):
if node is not None:
return node.height
return -1
def update_height(self, node):
node.height = max([self.height(node.left), self.height(node.right)]) + 1
# target = []
# target.append(self.height(node.left))
# target.append(self.height(node.right))
# node.height = max(target) + 1
# 节点平衡因子
# 节点的平衡因子(balance factor)定义为节点左子树的高度减去节点右子树的高度,同时规定空节点平衡因子为 0
# 我们同样将获取节点的平衡因子的功能封装成函数,方便后续使用
def balance_factor(self, node):
# 空节点平衡因子为 0
if node is None:
return 0
# 节点的平衡因子 = 左子树高度 - 右子树高度
return self.get_height(node.left) - self.get_height(node.right)
def right_rotate(self, node):
child = node.left
grand_child = child.right # 若没有就记成 None。
child.right = node
node.left = grand_child
self.update_height(node)
self.update_height(child)
return child
def left_rotate(self, node):
child = node.right
grand_child = child.left
child.left = node
node.right = grand_child
self.update_height(node)
self.update_height(child)
return child8.2.3 先左旋后右旋
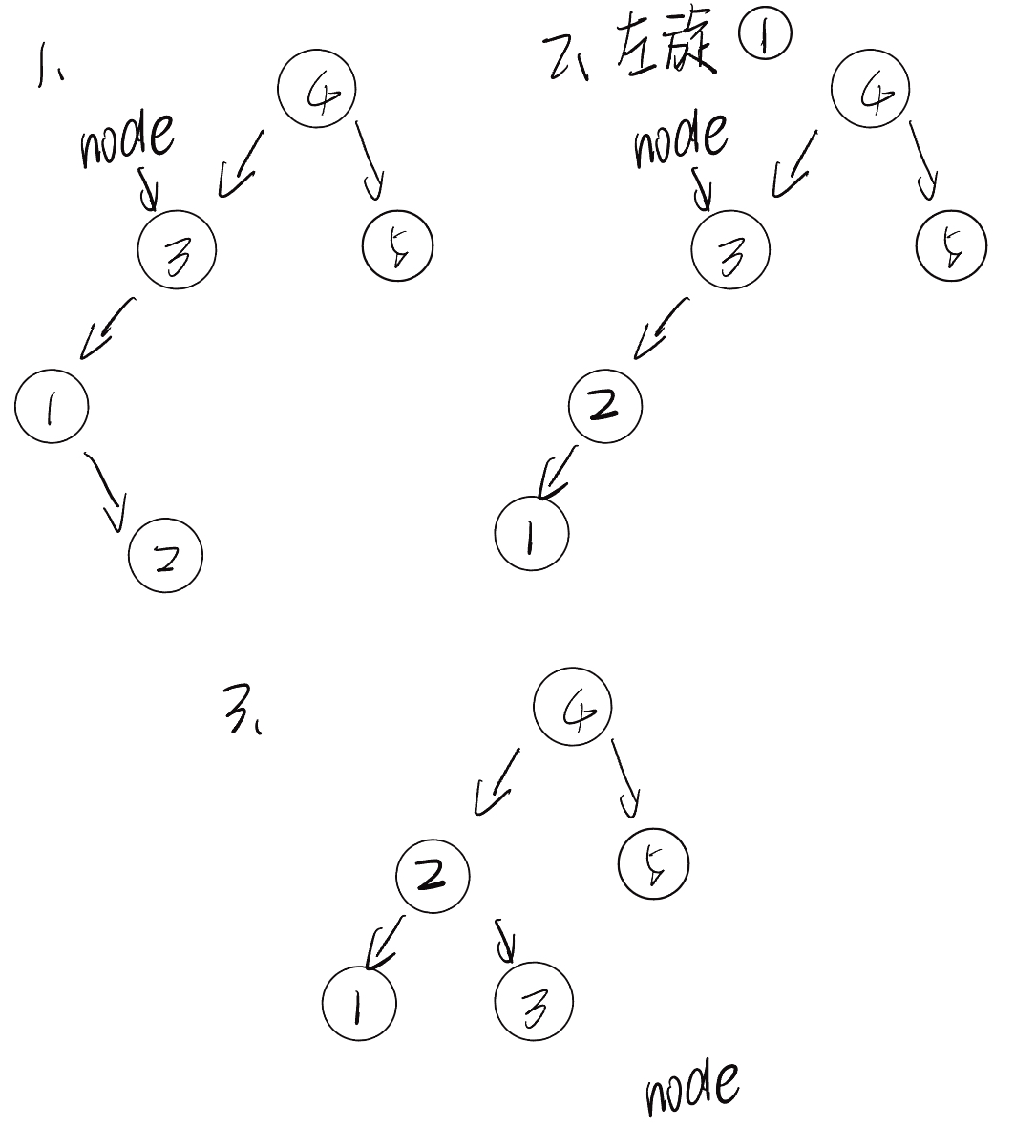
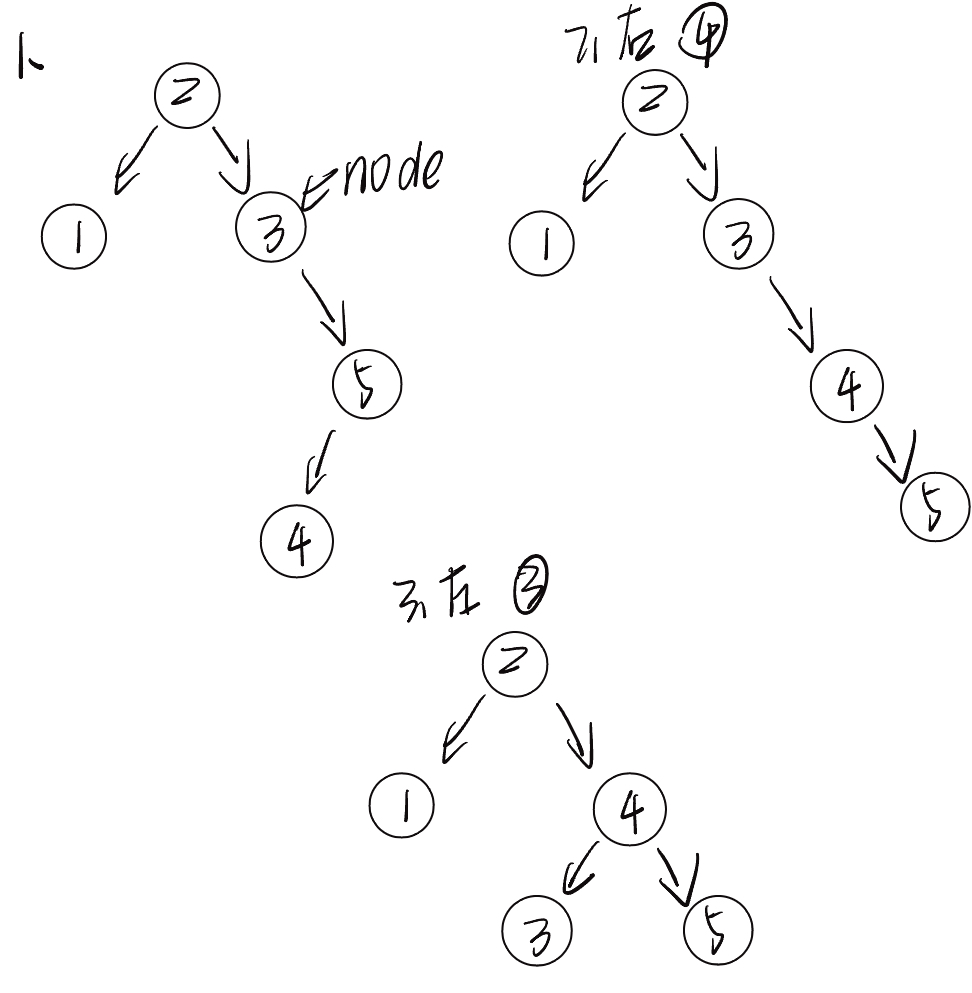
8.2.4 先右旋再左旋
8.2.5 完整代码
class TreeNode:
"""AVL 树节点类"""
# 该类用于表示 AVL 树的节点,包含节点的值、左右子节点的引用以及节点的高度
def __init__(self, val):
# 初始化节点时,设置节点值,并将左右子节点初始化为 None,节点高度初始为 0
self.val = val # 节点值
self.height = 0 # 节点高度,初始为 0
self.left = None # 左子节点引用,初始为 None
self.right = None # 右子节点引用,初始为 None
def get_height(self, node):
"""获取节点高度"""
# 如果节点存在,则返回节点的高度;否则返回 -1,表示空节点的高度
# 空节点高度为 -1 ,叶节点高度为 0
if node is not None:
return node.height # 返回节点的高度
return -1 # 空节点返回 -1
def update_height(self, node):
"""更新节点高度"""
# 节点的高度是左右子树中较高者的高度加 1
# 先获取左右子树的高度,更新当前节点的高度
node.height = max([self.get_height(node.left), self.get_height(node.right)]) + 1
# max([左子树高度, 右子树高度]) + 1
def balance_factor(self, node):
"""获取平衡因子"""
# 平衡因子是左右子树高度的差,用来判断子树的平衡情况
# 空节点平衡因子为 0
if node is None:
return 0 # 空节点返回 0
# 节点的平衡因子等于左子树的高度减去右子树的高度
return self.get_height(node.left) - self.get_height(node.right)
def right_rotate(self, node):
"""右旋操作"""
# 对于左偏的树执行右旋操作,使其重新平衡
child = node.left # 获取左子节点
grand_child = child.right # 获取左子节点的右子节点(孙节点)
# 以 child 为新根节点,将 node 作为 child 的右子节点
child.right = node # 原根节点变为右子节点
node.left = grand_child # 原左子节点的右子节点(孙节点)作为 node 的左子节点
# 更新旋转后节点的高度
self.update_height(node) # 更新原根节点的高度
self.update_height(child) # 更新新根节点的高度
# 返回旋转后的新根节点
return child # 右旋后返回新的子树根节点
def left_rotate(self, node):
"""左旋操作"""
# 对于右偏的树执行左旋操作,使其重新平衡
child = node.right # 获取右子节点
grand_child = child.left # 获取右子节点的左子节点(孙节点)
# 以 child 为新根节点,将 node 作为 child 的左子节点
child.left = node # 原根节点变为左子节点
node.right = grand_child # 原右子节点的左子节点(孙节点)作为 node 的右子节点
# 更新旋转后节点的高度
self.update_height(node) # 更新原根节点的高度
self.update_height(child) # 更新新根节点的高度
# 返回旋转后的新根节点
return child # 左旋后返回新的子树根节点
def rotate(self, node):
"""执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡"""
# 通过平衡因子判断当前子树是否失衡,若失衡则进行相应的旋转操作
balance_factor = self.balance_factor(node) # 获取节点的平衡因子
# 左偏树,平衡因子大于 1 表示左子树过高
if balance_factor > 1:
if self.balance_factor(node.left) >= 0:
# 左子树也是左偏:右旋恢复平衡
return self.right_rotate(node)
else:
# 左子树右偏:先对左子节点进行左旋,再右旋
node.left = self.left_rotate(node.left)
return self.right_rotate(node)
# 右偏树,平衡因子小于 -1 表示右子树过高
elif balance_factor < -1:
if self.balance_factor(node.right) <= 0:
# 右子树也是右偏:左旋恢复平衡
return self.left_rotate(node)
else:
# 右子树左偏:先对右子节点进行右旋,再左旋
node.right = self.right_rotate(node.right)
return self.left_rotate(node)
# 如果当前子树平衡,无需旋转,直接返回当前节点
return node # 平衡的子树直接返回8.2 AVL 树的插入
AVL 树的节点插入操作与二叉搜索树在主体上类似。唯一的区别在于,在 AVL 树中插入节点后,从该节点到根节点的路径上可能会出现一系列失衡节点。因此,我们需要从这个节点开始,自底向上执行旋转操作,使所有失衡节点恢复平衡。代码如下所示:
def insert(self, val):
"""插入节点"""
self._root = self.insert_helper(self._root, val)
def insert_helper(self, node: TreeNode | None, val: int) -> TreeNode:
"""递归插入节点(辅助方法)"""
if node is None:
return TreeNode(val)
# 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点
if val < node.val:
node.left = self.insert_helper(node.left, val)
elif val > node.val:
node.right = self.insert_helper(node.right, val)
else:
# 重复节点不插入,直接返回
return node
# 更新节点高度
self.update_height(node)
# 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
return self.rotate(node)8.2 AVL 树的删除
在 AVL 树的插入、删除和旋转操作中,通常只涉及对节点的引用的操作(即指针或引用的改变),并不会复制节点对象。这种行为可以被视为类似于浅拷贝的操作,因为在旋转、平衡等操作中,改变的是节点的引用关系,而不是复制整个子树或节点的内容。
类似地,在二叉搜索树的删除节点方法的基础上,需要从底至顶执行旋转操作,使所有失衡节点恢复平衡。代码如下所示:
def remove(self, val: int):
"""删除节点"""
self._root = self.remove_helper(self._root, val)
def remove_helper(self, node: TreeNode | None, val: int) -> TreeNode | None:
"""递归删除节点(辅助方法)"""
if node is None:
return None
# 1. 查找节点并删除
if val < node.val:
node.left = self.remove_helper(node.left, val)
elif val > node.val:
node.right = self.remove_helper(node.right, val)
else:
if node.left is None or node.right is None:
child = node.left or node.right
# 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if child is None:
return None
# 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else:
node = child
else:
# 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
temp = node.right
while temp.left is not None:
temp = temp.left
node.right = self.remove_helper(node.right, temp.val)
node.val = temp.val
# 更新节点高度
self.update_height(node)
# 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
return self.rotate(node)