高级算法——第2,3周查漏补缺
原创2024年11月5日大约 3 分钟
Week 02: Sorting Algorithms
1. Bogosort
import random
def bogoSort(mylist):
while (is_sorted(mylist) == False): # if the list is not sorted...
shuffle(mylist) # ...shuffle again
return (mylist) # if sorted, return
# check if list is sorted
def is_sorted(mylist):
n = len(mylist)
for i in range(0, n - 1): # iterate through list
if (mylist[i] > mylist[i + 1]): # if number is bigger than the number to the right
return False # list is not sorted so return False
# shuffle the list
def shuffle(mylist):
n = len(mylist)
for i in range(0, n):
r = random.randint(0, n - 1) # go through list, swapping each
mylist[i], mylist[r] = mylist[r], mylist[i] # item with another randomly chosen
# item
mylist = [3, 2, 4, 1, 0, 5] # define a list to sort
print(bogoSort(mylist)) # function call2. Insertion Sort
def insertionsort(arr):
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
key = arr[i]
j = i
while j > 0 and arr[j - 1] > key:
arr[j] = arr[j - 1]
j = j - 1
arr[j] = key
return arr
print(insertionsort([10, 6, 11, 2, 9]))3. Bubble Sort
def bubble_sort(arr):
for i in range(len(arr)):
for j in range(len(arr) - i - 1):
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
return arr
print(bubble_sort([4,6,1,7,3]))4. Quick Sort
def quick_sort(arr):
if arr == []:
return
pivot = arr[0]
ltp = []
etogtp = []
for x in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[x] < pivot:
ltp.append(x)
else:
etogtp.append(x)
return quick_sort(ltp) + [pivot] + quick_sort(etogtp)
print(quick_sort([1, 4, 2, 7, 5, 9]))5. merge sort
def merge_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
mid = len(arr) // 2
left_arr = arr[:mid]
right_arr = arr[mid:]
left_sort = merge_sort(left_arr)
right_sort = merge_sort(right_arr)
merged = merge(left_sort, right_sort)
return merged
def merge(left_arr, right_arr):
result = []
i = j = 0
while i < len(left_arr) and j < len(right_arr):
if left_arr[i] < right_arr[j]:
result.append(left_arr[i])
i += 1
else:
result.append(right_arr[j])
j += 1
result.extend(left_arr[i:])
result.extend(right_arr[j:])
return result
print(merge_sort([38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10]))Week 03
1. Linear Search
- Also called sequential search
- Iterate over elements until found or sequence ends
Disadvantages:
- Not a very good algorithm
- We have to check every single item in sequence
- Inefficient
Code:
def linear(lst, goal_num):
for i in range(len(lst)):
if lst[i] == goal_num:
return i
else:
return -1
print(linear([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 2))2. Binary Search
- Much faster than linear search
- A ‘Divide and Conquer’ algorithm
- Only works on sorted sequences
2.1 How it works?
- Find the middle value of sequence
- If search value is the middle value, then success
- If search value is less than the middle value, discard the top half of the sequence
- If search value is greater than the middle value, discard the bottom half of the sequence
- Repeat from (1) until value is found or length of the sequence is zero (i.e. value is not found)
Iterative
def binarySearch(arr, val):
middle = len(arr) // 2
while val != arr[middle]:
if len(arr) > 1:
if arr[middle] > val:
arr = arr[0:middle]
else:
arr = arr[middle:]
else:
if val != arr[middle]:
return False
middle = len(arr) // 2
return True
print(binarySearch([1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10], 8))Recursive
def binarySearch(arr, val):
ans = True
if len(arr) == 1 and val != arr[0]:
ans = False
else:
middle = len(arr) // 2
if val != arr[middle]:
if val > arr[middle]:
arr = arr[middle + 1:]
ans = binarySearch(arr, val)
else:
arr = arr[:middle]
ans = binarySearch(arr, val)
return ans
print(binarySearch([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], 6))自己写的代码
def binarySearch(arr, val):
i = 0
j = len(arr) - 1
while i <= j:
middle = (i + j) // 2
if arr[middle] == val:
return True
elif arr[middle] > val:
j = middle - 1
elif arr[middle] < val:
i = middle + 1
return False
print(binarySearch([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], 6))3. Interpolation Search
给定一个长度为 n 的有序数组 nums 和一个元素 target ,数组不存在重复元素。现将 target 插入数组 nums 中,并保持其有序性。若数组中已存在元素 target ,则插入到其左方。请返回插入后 target 在数组中的索引。
def binary_searching(nums, target):
i = 0
j = len(nums) - 1
while i <= j:
m = (i + j) // 2
if nums[m] == target:
nums.insert(m, target)
return nums
elif nums[m] > target:
j = m - 1
else:
i = m + 1
else:
return i
print(binary_searching([1, 3, 6, 8, 12, 15, 23, 26, 31, 36], 6))4. Data Structures
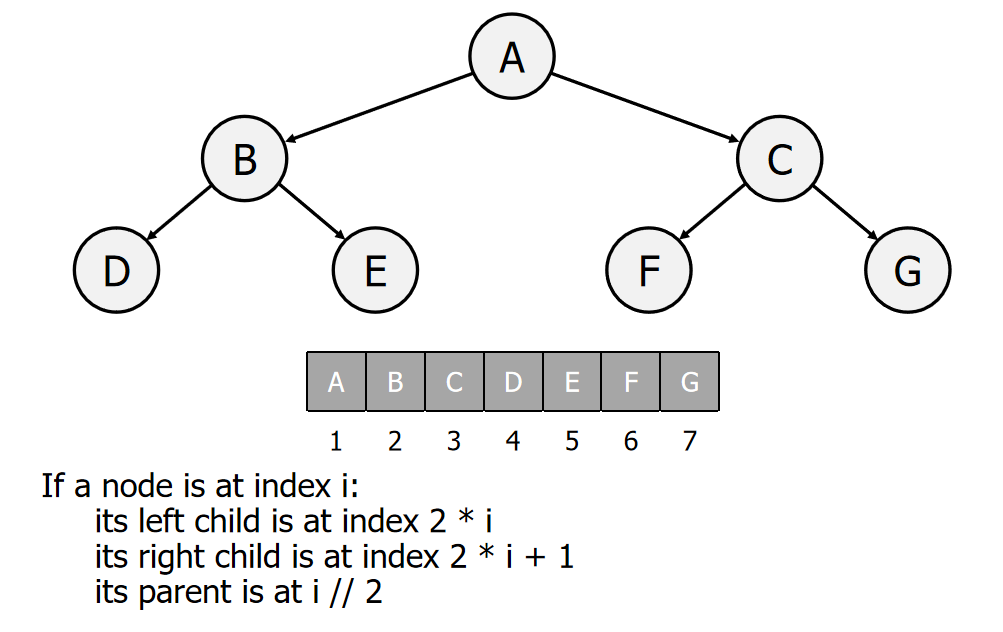
4.1 Binary Tree
Some Rules