RNN模型训练
原创2025年4月14日大约 3 分钟
初始参数
import os
import math
import random
import urllib.request
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# =========================
# 自动下载数据
# =========================
file_path = "timemachine.txt"
url = "http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/timemachine.txt"
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print("Downloading dataset...")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, file_path)
# =========================
# 数据预处理
# =========================
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
text = f.read().lower()
text = ''.join([line.strip() for line in text.split('\n') if line.strip()])
# 构建词表
vocab = sorted(list(set(text)))
vocab_size = len(vocab)
char2idx = {ch: i for i, ch in enumerate(vocab)}
idx2char = {i: ch for i, ch in enumerate(vocab)}
corpus = [char2idx[ch] for ch in text]
# =========================
# 获取 mini-batch 数据
# =========================
def get_batch(corpus, batch_size, num_steps):
start = random.randint(0, len(corpus) - batch_size * num_steps - 1)
inputs, targets = [], []
for i in range(batch_size):
idx = start + i * num_steps
inputs.append(corpus[idx:idx + num_steps])
targets.append(corpus[idx + 1:idx + num_steps + 1])
return torch.tensor(inputs), torch.tensor(targets)
# =========================
# RNN 模型定义
# =========================
class RNNModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, vocab_size) # one-hot
self.rnn = nn.RNN(vocab_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size)
def forward(self, x, state):
x = self.embedding(x)
out, state = self.rnn(x, state)
out = self.fc(out)
return out, state
def init_state(self, batch_size):
return torch.zeros(1, batch_size, hidden_size)
# =========================
# 模型训练函数
# =========================
def train(model, corpus, num_epochs, batch_size, num_steps, lr):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
perplexities = []
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
state = model.init_state(batch_size)
X, Y = get_batch(corpus, batch_size, num_steps)
Y = Y.reshape(-1)
logits, state = model(X, state)
logits = logits.reshape(-1, vocab_size)
loss = loss_fn(logits, Y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
ppl = math.exp(loss.item())
perplexities.append(ppl)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss {loss.item():.4f}, Perplexity {ppl:.2f}")
return perplexities
# =========================
# 参数设置 & 启动训练
# =========================
hidden_size = 128
batch_size = 32
num_steps = 35
lr = 1e-2
num_epochs = 20
model = RNNModel(vocab_size, hidden_size)
perplexity_list = train(model, corpus, num_epochs, batch_size, num_steps, lr)
# =========================
# 绘制 Perplexity 折线图
# =========================
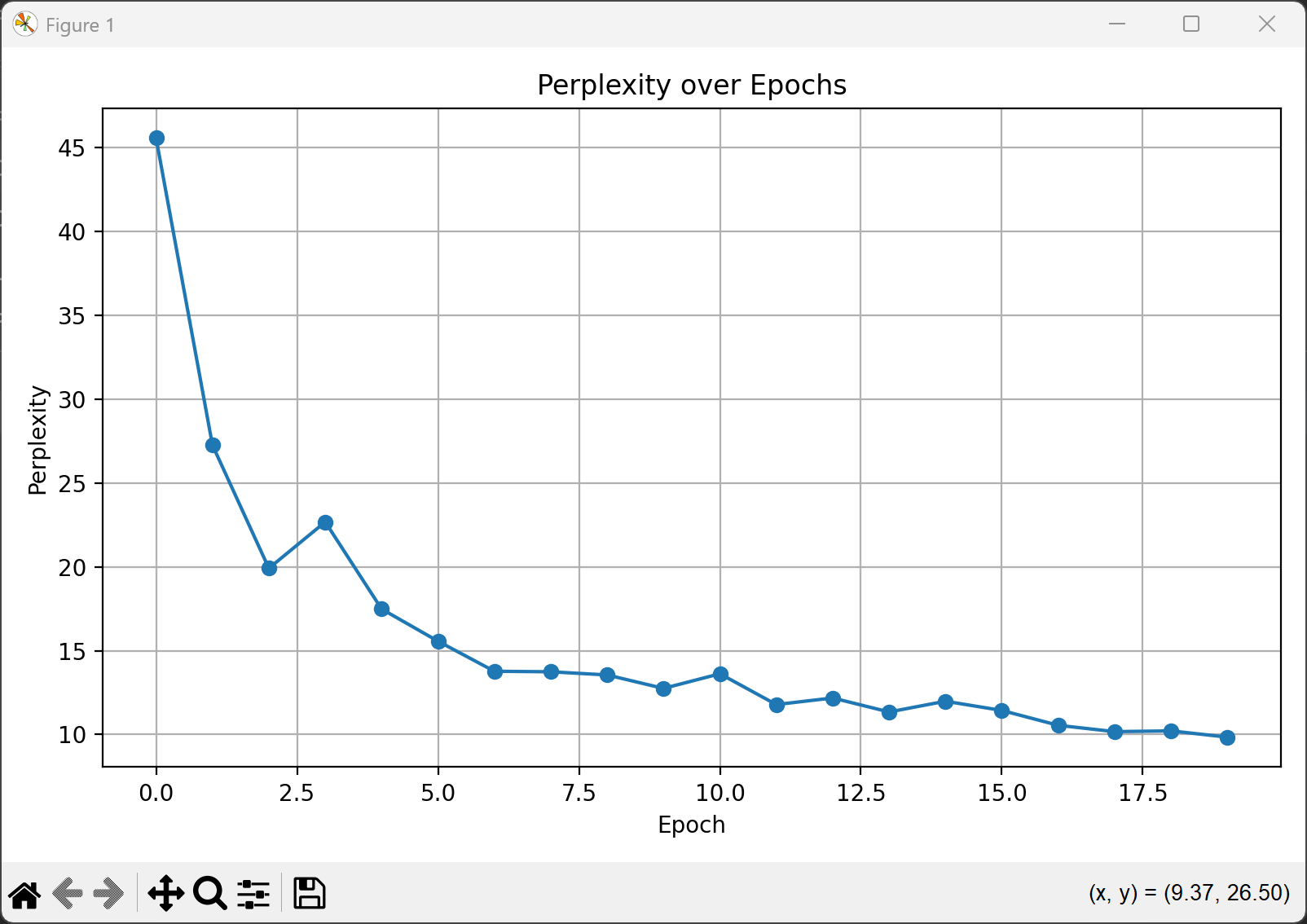
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.plot(perplexity_list, marker='o')
plt.title("Perplexity over Epochs")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("Perplexity")
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("perplexity_plot.png")
plt.show()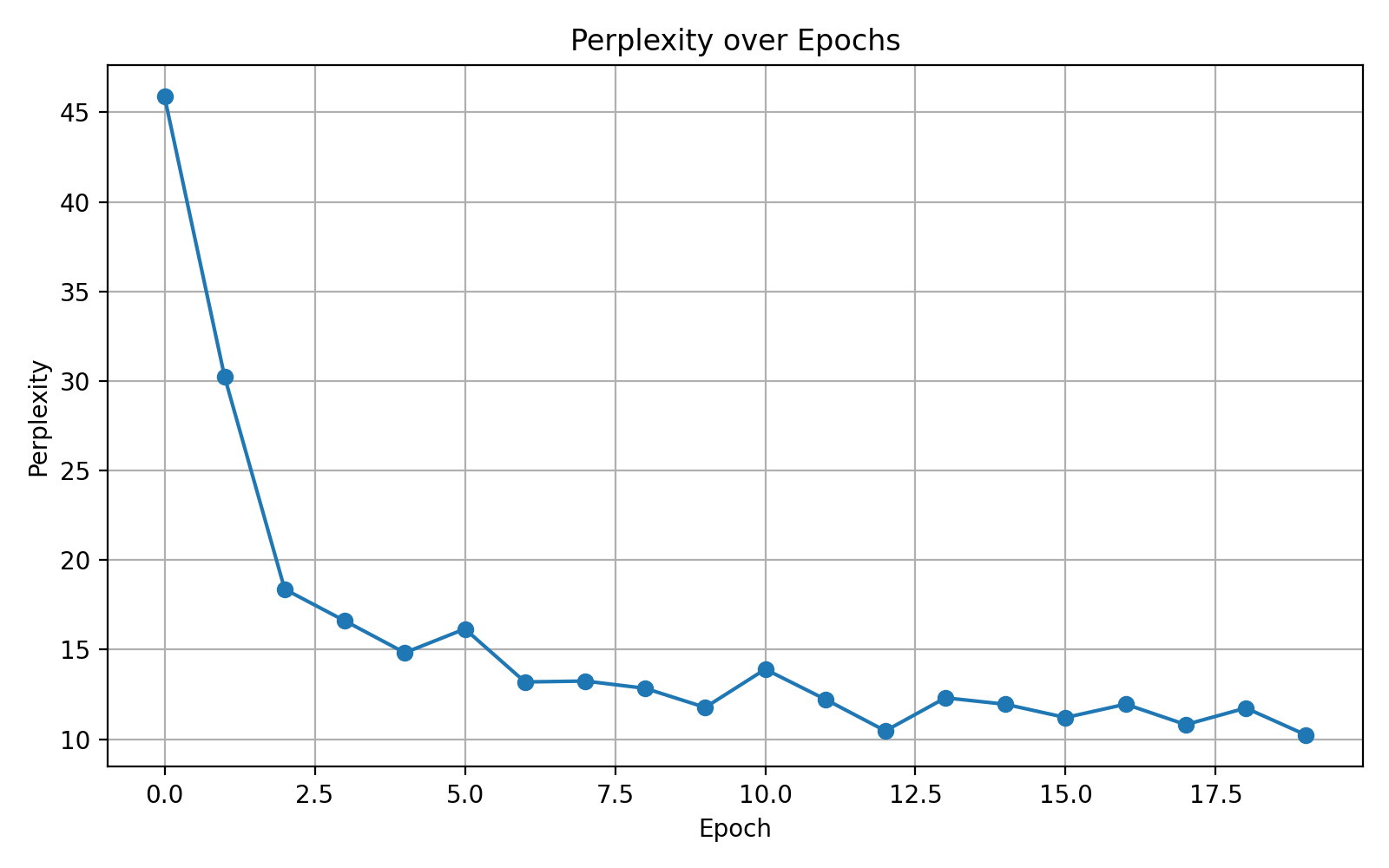
改变隐藏层维度
提高至 200:
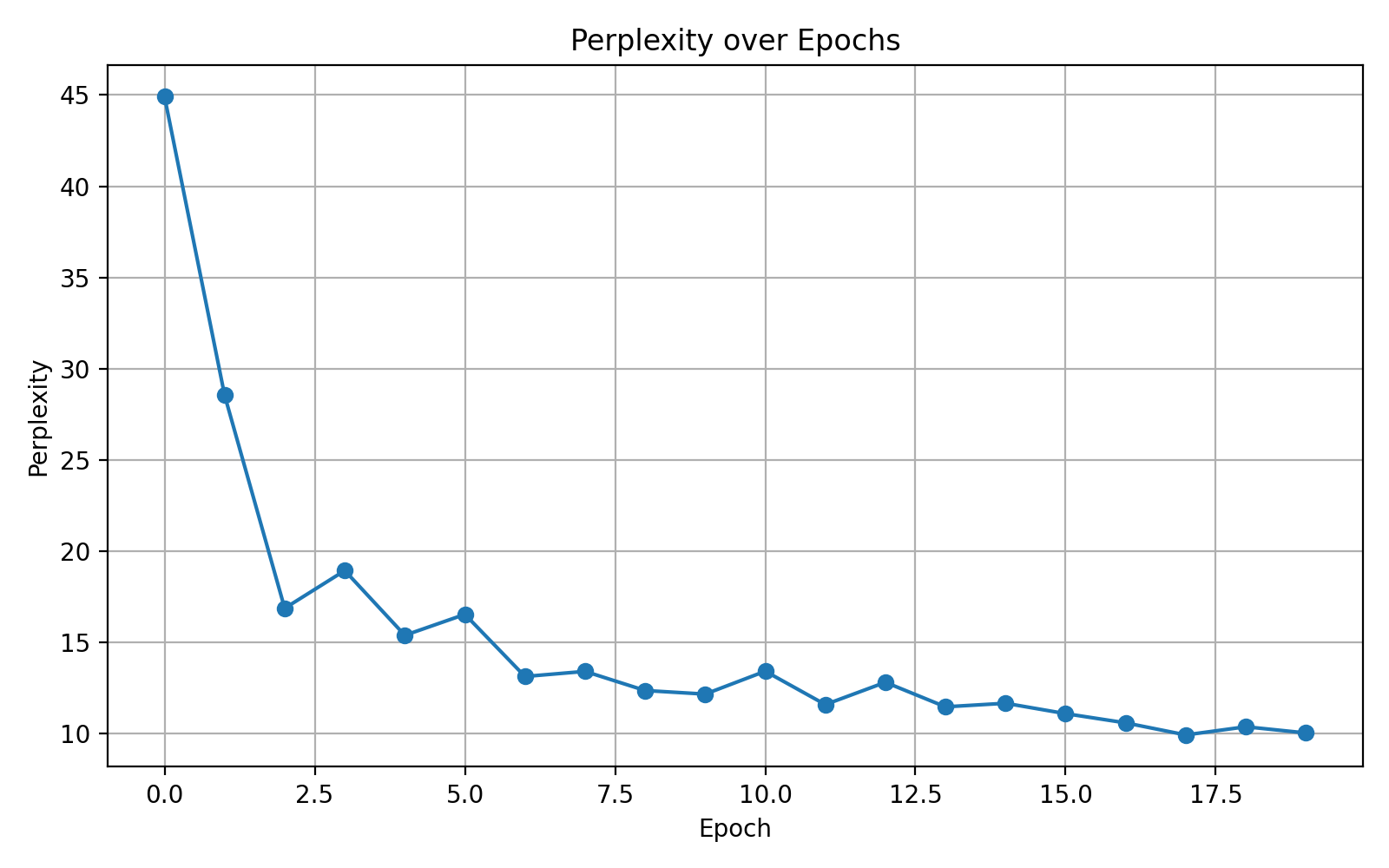
提高至 300:
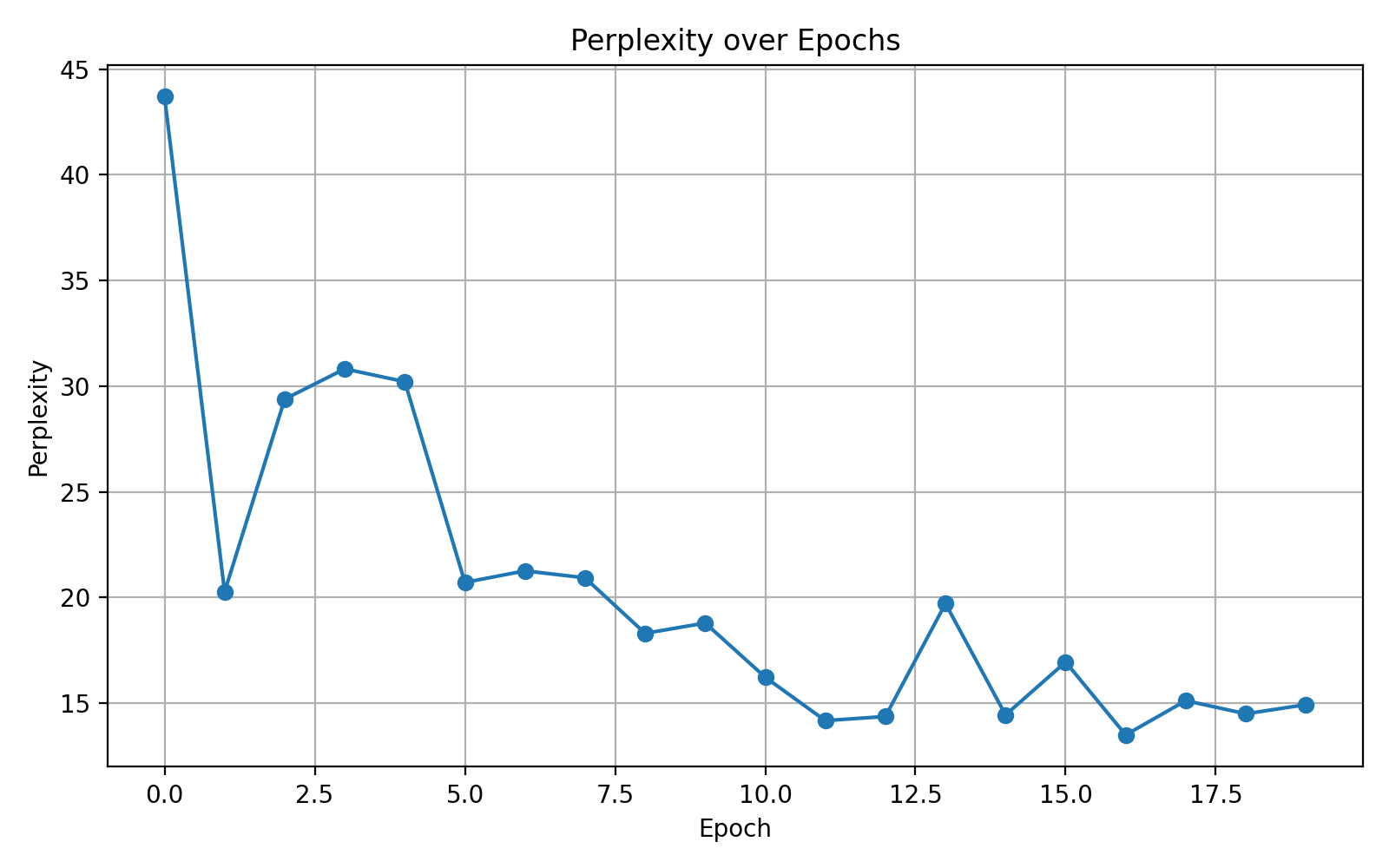
| 维度 | 影响 |
|---|---|
| 小(128) | 记忆力中等,学习稳定,但不够强 |
| 中(200) | 记忆力加强,捕捉依赖能力提升,表现更好 ✅ |
| 大(300) | 参数数目更多,训练难度加大,可能不容易收敛或震荡 |
我们选择最优参数,进一步调其他参数看看能不能越来越好。
调整批量大小:
32 调整为 16:
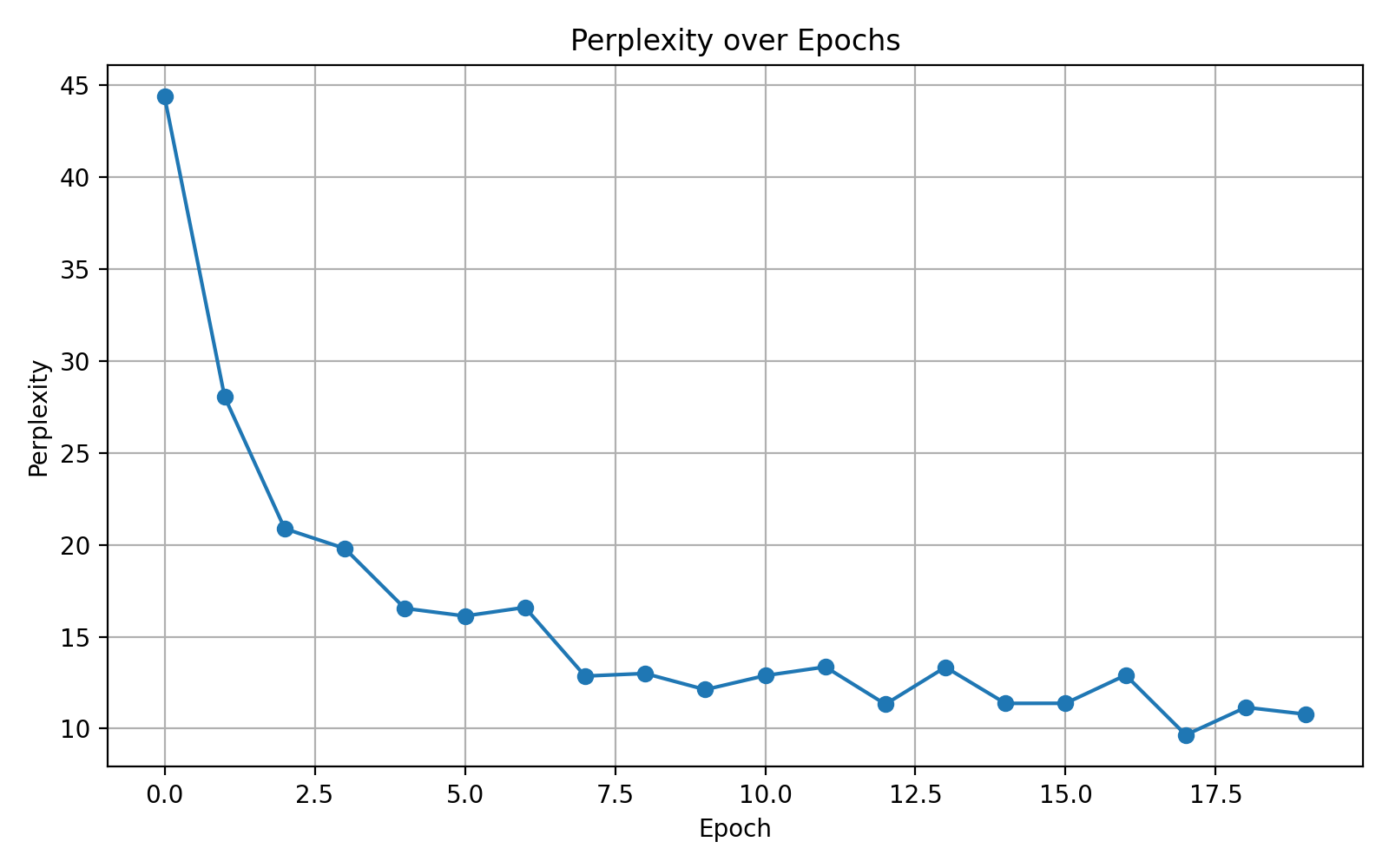
32 调整为 64:
| Batch Size | 收敛速度 | 波动性 | 最终 perplexity | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 很快 | 明显波动 | 10 左右 | 梯度噪声大,更随机 |
| 32 | 中等 | 偏稳定 | 最佳平衡点 ✅ | 实用性强 |
| 64 | 稳定但慢 | 极平稳 | 与32相近 | 占用内存高,适合大模型 |
所以批量大小不在原有基础上修改。
🧮 给定条件:
- 输入序列长度:5(不影响参数量,只影响运算步数)
- 输入维度
- 隐藏层数:2 层
- 每层隐藏单元数:3 个神经元
- 输出维度:1(每个时间步输出 1 维)
- 使用标准 RNN 单元(假设是 vanilla RNN)
✅ 分层计算参数量:
🔹 第一层 RNN(Layer 1):
输入维度:1
隐藏维度:3
RNN 的参数包括:
合计:
🔹 第二层 RNN(Layer 2):
输入维度:上层隐藏输出是 3
隐藏维度:3
合计:
🔹 输出层(对每个时间步):
- 输入是第 2 层的隐藏状态:3 维
- 输出是 1 维
- 所以:
合计:
✅ 总参数量:
第一层 + 第二层 + 输出层
✅ 最终总参数量是: 40
如你使用的是 LSTM 或 GRU,参数会更多,需要分别计算门控结构。如果你需要计算 GRU/LSTM 的参数,我也可以帮你列出来!
